The Real Science Behind Olive Oil's Digestive Power
Olive oil has long been praised for its health benefits, but its positive effects on digestion are often overlooked. Let's delve into the science behind olive oil's digestive power, moving beyond anecdotal evidence to understand how it truly benefits your gut. This exploration reveals why this "liquid gold" has been a cornerstone of digestive health for centuries.
How Olive Oil Benefits Your Gut Microbiome
A crucial aspect of digestive health is the balance of your gut microbiome, the complex community of microorganisms residing in your digestive tract. Olive oil, particularly extra-virgin olive oil (EVOO), plays a significant role in nurturing this delicate ecosystem. It promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bacteroides, essential for producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs).
These SCFAs act as fuel for the cells lining your gut, strengthening the intestinal barrier and supporting a healthy immune response. This, in turn, leads to reduced inflammation and improved overall digestive function. Extra virgin olive oil has been a staple in Mediterranean diets for centuries, with its digestive benefits long acknowledged.
Studies have shown that EVOO can enhance the growth of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bacteroides, which are crucial for SCFA production. These SCFAs are essential for maintaining the gut lining and supporting the immune system. Research indicates that the polyphenols in olive oil, not just the fatty acids, contribute significantly to its digestive and overall health benefits.
The Role of Polyphenols and Fatty Acids
The power of olive oil lies in its unique composition of polyphenols and healthy fatty acids. Polyphenols act as potent antioxidants, protecting your gut lining from damage caused by free radicals. They act as a defense mechanism for your digestive system.
This protective action helps maintain the integrity of your intestinal wall, preventing leaky gut and promoting efficient nutrient absorption. The healthy fats in olive oil, primarily monounsaturated fats, lubricate the digestive tract.
This lubrication facilitates smoother movement of food through the intestines, reducing the likelihood of constipation and promoting regular bowel movements. Polyphenols and fatty acids work together to optimize your digestive environment.
Olive Oil's Impact on Nutrient Absorption
In addition to supporting a healthy gut microbiome and lubricating the digestive tract, olive oil enhances nutrient absorption. By improving the health and integrity of your intestinal lining, olive oil allows your body to effectively absorb vital nutrients from food.
This maximized nutritional benefit supports overall health and well-being. Improved absorption is crucial for maintaining optimal energy levels, supporting immune function, and promoting healthy cell growth and repair.
How Olive Oil Supports Your Liver And Gallbladder

Your liver and gallbladder play vital roles in digestion, processing fats and removing waste. Olive oil, thanks to its unique composition, provides significant support for these important organs. Incorporating olive oil into your diet can contribute to overall digestive wellness, impacting more than just your gut.
Olive Oil: A Natural Aid for Bile Flow
Olive oil functions as a cholagogue, a substance that promotes healthy bile flow from the gallbladder. Bile is essential for fat digestion, but it can sometimes crystallize, forming gallstones. The steady flow of bile stimulated by olive oil helps prevent this crystallization. This ensures that fats are properly emulsified and absorbed by the body. This consistent bile flow also helps reduce the risk of gallstones, a painful and potentially serious condition.
Liver-Loving Properties of Olive Oil
Olive oil’s benefits extend beyond promoting bile flow. It also supports liver health in multiple ways. For instance, olive oil stimulates the liver's production of bile salts. These are crucial for breaking down fats and absorbing fat-soluble vitamins. Furthermore, olive oil promotes the excretion of cholesterol, contributing to a healthier liver and further mitigating the risk of gallstones. You can explore this topic further at International Olive Oil.
Pancreatic Support Through Olive Oil
Olive oil is especially beneficial for individuals with pancreatic sensitivities. Unlike other fats that require substantial pancreatic enzyme secretion for digestion, olive oil is relatively easy to digest. This reduced workload on the pancreas makes olive oil a valuable addition to a digestion-friendly diet, especially for those with pancreatic disorders. Olive oil provides a gentle and supportive approach to maintaining pancreatic health. It allows the pancreas to function without being overburdened.
What Mediterranean Populations Teach Us About Digestive Health

Scientific evidence supporting the digestive benefits of olive oil is strong, but real-world examples offer even more compelling insights. Consider the populations of Mediterranean countries, where olive oil is a fundamental part of their diet. These regions provide a practical demonstration of the long-term advantages of regular olive oil consumption. This naturally leads us to explore the significant impact of cultural dietary habits on digestive well-being.
Lower Rates of Digestive Disorders
In countries like Greece and Italy, where olive oil is deeply integrated into daily meals, the occurrence of digestive disorders is notably lower compared to regions where olive oil is consumed less frequently. This contrast is not random. These populations offer valuable lessons on the connection between diet and digestive health. The reduced prevalence of digestive issues suggests a protective effect associated with olive oil.
This protective effect extends beyond the digestive system. Studies have shown a correlation between olive oil consumption and improved health outcomes worldwide. For instance, the Mediterranean diet, abundant in olive oil, has been linked to a 30% reduction in cardiovascular disease risk and a 13% reduction in overall mortality. Find more detailed statistics here. This data underscores the broader health benefits of olive oil. It emphasizes the significant role of dietary choices in achieving long-term wellness.
A Cornerstone of Healthy Living
The positive outcomes observed in Mediterranean populations highlight the value of including olive oil in a healthy lifestyle. This is not solely about addressing existing digestive problems; it's also about proactive prevention. These observations suggest that consistent olive oil consumption may contribute to preventing digestive health issues.
Moreover, the Mediterranean diet, with olive oil as a central element, presents a comprehensive approach to wellness. It provides valuable insights into sustainable health practices. It emphasizes whole foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with olive oil. This combined approach benefits not only digestive health but also cardiovascular health, metabolic function, and overall lifespan. These combined benefits position olive oil as a true cornerstone of healthy living. The wider range of health improvements underscores the positive impact of a balanced, olive oil-rich diet.
Choosing The Right Olive Oil For Your Digestive Goals
Not all olive oils offer the same digestive health benefits. Understanding the differences is crucial for selecting the right oil for your specific needs. Making informed choices can significantly improve your digestive health.
Decoding Olive Oil Labels
When choosing olive oil, start by understanding the labels. Look for "extra-virgin olive oil (EVOO)". This signifies the highest quality, meaning the oil was cold-pressed without heat or chemicals. This preserves the polyphenols, potent antioxidants vital for digestive health. Also, check the origin and harvest date for optimal freshness.
Quality Indicators That Matter
Beyond the label, several factors indicate quality. A deep green color often suggests a higher concentration of beneficial compounds. However, aroma and taste are also important. High-quality EVOO has a fruity, peppery flavor. A rancid or bland taste suggests degradation. Choose oil in dark glass bottles to protect it from light and oxidation.
Processing Methods and Their Impact
Processing methods directly impact an olive oil's composition and digestive benefits. Cold-pressing is the gold standard, avoiding heat and chemicals that degrade polyphenols. Other methods may strip away beneficial compounds. Choosing cold-pressed EVOO maximizes digestive benefits, ensuring the oil retains its health-promoting components.
Storage Techniques To Preserve Digestive Properties
Proper storage is crucial. Keep olive oil in a cool, dark place away from heat and light. Exposure to these elements can cause oxidation, reducing quality and digestive benefits. Proper storage protects your investment and ensures you receive the full benefits.
To help you better understand the different types of olive oil and their respective benefits, take a look at the table below:
Olive Oil Types And Digestive Benefits Comparison: A detailed comparison of different olive oil types, their processing methods, polyphenol content, and specific digestive health benefits
| Oil Type | Processing Method | Polyphenol Content | Digestive Benefits | Best Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) | Cold-pressed | Highest | Rich in antioxidants, supports gut health, reduces inflammation | Salad dressings, dipping, finishing dishes |
| Virgin Olive Oil | Cold-pressed | Medium | Contains antioxidants, promotes healthy digestion | Cooking, baking |
| Refined Olive Oil | Refined & blended with virgin olive oil | Low | Neutral flavor, suitable for high-heat cooking | Frying, sautéing |
| Olive Pomace Oil | Solvent extraction | Lowest | Not recommended for digestive health benefits | Industrial uses |
This table summarizes the key characteristics and benefits of each olive oil type. Choosing EVOO is generally recommended for maximizing digestive health advantages.
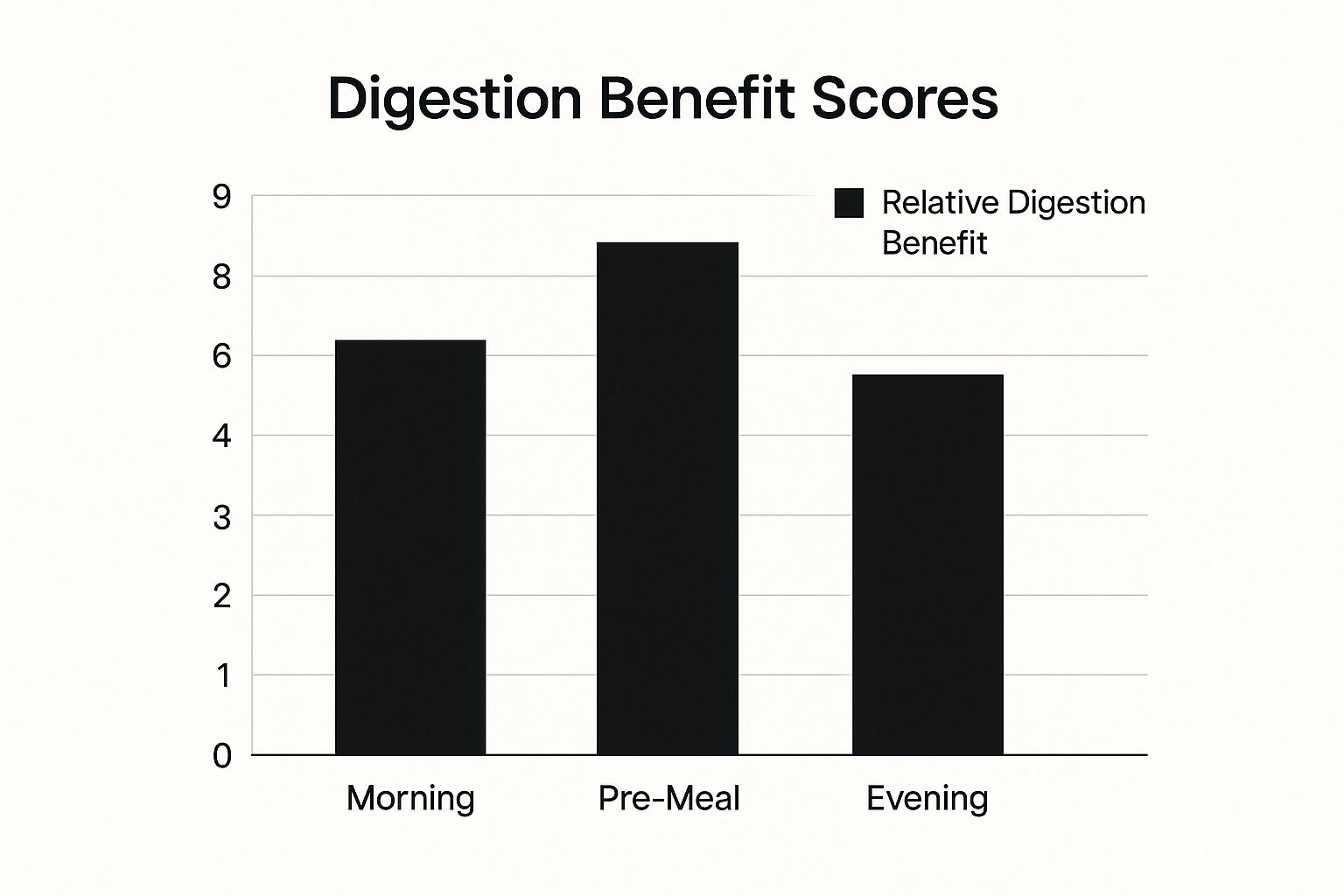
The infographic above illustrates the relative digestive benefits of consuming olive oil at different times. Consuming olive oil before meals provides the greatest potential benefit, followed by morning consumption. Strategically timing your intake can optimize its impact on your digestive system. Learn more about the benefits of olive oil
Making Olive Oil Work In Your Daily Routine

Adding olive oil to your daily routine doesn't have to mean a complete diet change. Instead, concentrate on easy and practical ways to include it in your current habits. This section provides research-backed advice on timing, dosage, and ways to use olive oil in your cooking. Learn how to get the most digestive benefits from olive oil without sacrificing taste or convenience.
Timing Your Olive Oil Intake for Optimal Digestion
When you consume olive oil can greatly affect how well it works. While there isn't one perfect time, certain times of day offer better digestive benefits. Consider these options:
-
Morning Routine: Beginning your day with a tablespoon of high-quality extra virgin olive oil can stimulate bile production and encourage regular bowel movements. This can be particularly beneficial for those who experience constipation in the morning.
-
Pre-Meal Consumption: Having a small amount of olive oil before meals can get your digestive system ready for food. The oil coats the stomach lining, which may reduce irritation and help with smoother digestion. This practice may also improve how your body absorbs nutrients from your meal.
-
Cooking with Olive Oil: Using olive oil for cooking adds flavor and offers digestive benefits. Choose cooking methods that keep the oil's helpful properties intact. Low-heat cooking methods like sautéing or baking are ideal. Avoid frying at high temperatures, as this can harm the oil's beneficial compounds.
Incorporating Olive Oil Into Your Meals
Adding olive oil to your meals is easier than you think. Here are a few simple ways to make it a regular part of your diet:
-
Salads and Vegetables: Drizzle olive oil over salads and roasted vegetables. The rich flavor pairs well with fresh produce.
-
Dipping Bread: Try the traditional Mediterranean custom of dipping crusty bread into olive oil mixed with herbs or spices.
-
Soups and Stews: A swirl of olive oil in soups and stews adds a flavorful touch and some extra digestive support.
-
Marinades: Olive oil makes a great base for marinades for fish, chicken, or tofu. It adds flavor, tenderizes the food, and provides digestive benefits.
Dosage and Gradual Introduction
Begin by adding one to two tablespoons of olive oil to your daily routine. Gradually increase this amount as your body adapts. Pay close attention to how your body feels. Some people might have mild digestive discomfort if they increase their olive oil intake too rapidly.
Realistic Meal Planning and Portion Control
You don't need to make huge changes to your meal plans to incorporate olive oil. Small adjustments can make a significant difference. For example, switch from butter or other cooking oils to olive oil. Use it to make salad dressings. Drizzle it over cooked vegetables. These simple changes can effectively add olive oil to your daily diet without changing your meals too much or requiring complicated recipes.
Learn more about incorporating olive oil at Learn Olive Oil. By using these practical tips, you can easily benefit from the digestive power of olive oil and enjoy its many health advantages.
Potential Side Effects and Smart Precautions
While olive oil offers a wealth of digestive benefits, it’s important to understand the potential side effects and necessary precautions. Smart usage begins with being fully informed. This empowers you to maximize the advantages while minimizing any potential risks.
Caloric Content and Moderation
Olive oil, like any oil, is calorie-dense. A single tablespoon contains approximately 120 calories. While beneficial for digestion, overconsumption can lead to weight gain. Moderation is crucial for enjoying olive oil's digestive benefits without negatively impacting your caloric intake.
Olive oil is a potent tool, effective when used correctly, but potentially problematic in excess.
Potential Medication Interactions
Olive oil has the potential to interact with certain medications, particularly those prescribed for blood sugar control and blood thinning. If you are currently taking medication, it’s vital to consult your doctor before significantly increasing your olive oil intake. This proactive step helps ensure safe and effective usage within your current health management plan. Combining olive oil with medications without professional guidance could lead to unforeseen consequences.
Recognizing Signs of Overconsumption
Although olive oil is generally safe, excessive consumption can cause digestive upset, such as diarrhea and stomach cramps. Start slowly when incorporating olive oil into your diet. Listen to your body’s feedback. If you experience any adverse reactions after increasing your intake, reduce the amount to a comfortable level. This attentive approach helps you find the right balance for your individual digestive system. Your body provides valuable feedback – pay attention to its signals.
Individuals With Specific Digestive Conditions
Individuals with gallbladder problems or pancreatitis should exercise extra caution with olive oil and consult their healthcare provider. While olive oil may benefit some digestive issues, it could potentially worsen others. A personalized approach is critical for individuals with pre-existing conditions. Professional guidance ensures that olive oil supports, rather than hinders, their health. Remember, olive oil is a powerful tool, but it must be used appropriately.
Consulting Your Healthcare Provider
For personalized advice regarding the incorporation of olive oil into your health regimen, consult with a healthcare professional. They can offer tailored recommendations based on your specific health status and needs. This personalized guidance ensures you’re maximizing the benefits of olive oil while minimizing any potential risks. Informed choices empower you to take control of your digestive health. Collaborating with your healthcare provider provides valuable insights and guarantees safe and effective use of olive oil as part of your overall wellness plan.
Your Action Plan For Digestive Wellness Success
This section provides a roadmap for safely incorporating olive oil into your daily routine for improved digestive health. We'll cover practical steps, realistic expectations, and simple tracking methods to monitor your progress. It's where knowledge translates into action.
Getting Started With Olive Oil for Digestion
Begin by choosing high-quality extra virgin olive oil (EVOO). Look for cold-pressed oil packaged in dark glass bottles to protect its beneficial properties. Start with a modest amount of one to two tablespoons daily, gradually increasing the intake as your body adjusts. Consider various ways to incorporate olive oil into your diet, such as using it in salad dressings, dips, or drizzled over cooked vegetables. Carefully monitor your digestion for any changes, whether positive or negative.
Setting Realistic Expectations and Tracking Progress
Remember, improvements in digestion can be subtle and gradual. Don't expect immediate changes. Consistency is key to experiencing the benefits of olive oil. Maintain a digestive health journal to track your bowel movements, bloating, and any discomfort. Over time, you may observe improved regularity, reduced bloating, and less overall digestive discomfort. This consistent tracking provides valuable insights into how your body responds to olive oil.
Daily Consumption Strategies and Warning Signs
Experiment with different consumption times to find what works best for you. Some individuals find morning consumption beneficial for promoting bowel regularity, while others prefer taking it before meals to support digestion. Pay attention to your body's signals. If you experience any negative side effects, such as diarrhea or stomach cramps, reduce your olive oil intake accordingly. This personalized approach allows you to determine the optimal amount and timing that suits your body's specific needs.
Olive Oil Selection Checklist
To help you select the right olive oil, here's a quick checklist:
- Look for "extra-virgin olive oil": This designation signifies the highest quality and minimal processing, ensuring you're getting the most benefits.
- Check for "cold-pressed": This extraction method preserves the beneficial compounds and antioxidants found in olives.
- Choose dark glass bottles: Dark glass protects the oil from light and oxidation, maintaining its freshness and quality.
- Consider the harvest date: Fresher oil typically has a richer flavor and higher antioxidant content.
To further assist you in optimizing your olive oil intake, let's examine some specific guidelines based on your health goals:
Daily Olive Oil Consumption Guidelines For Digestive Health
| Health Goal | Daily Amount | Best Timing | Consumption Method | Expected Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Improved Bowel Regularity | 1-2 tablespoons | Morning | With warm water or on an empty stomach | 1-2 weeks |
| Enhanced Digestion | 1 tablespoon | Before meals | Drizzled over food or as a salad dressing | A few days – 1 week |
| Reduced Bloating | 1-2 tablespoons | Throughout the day | Incorporated into meals (salads, dips, cooking) | 1-2 weeks |
This table summarizes the recommended daily amounts, optimal timing, and effective consumption methods for achieving various digestive health goals. The expected timeline provides a general timeframe for noticing potential benefits, though individual results may vary.
By following these guidelines and making informed decisions, you can effectively utilize olive oil to enhance your digestive well-being. Begin your journey towards a healthier gut today!
Ready to delve deeper into the world of high-quality olive oil? Visit Learn Olive Oil to explore premium options and elevate your digestive health journey.

Leave a comment