The Truth About Olive Oil's Smoking Point
Olive oil. A kitchen staple, a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet, and yet, often misunderstood. One of the most common misconceptions revolves around its smoking point. Let's dispel the myths and uncover the facts about this culinary treasure.
What Exactly Is a Smoking Point?
The smoking point of an oil is the temperature at which it begins to break down, visibly producing smoke and imparting a burnt flavor to food. This degradation not only affects taste but also diminishes the oil's nutritional value. Choosing the right oil with an appropriate smoking point is crucial for different cooking methods.
Dispelling the Myths Surrounding Olive Oil
Many believe that olive oil has too low a smoking point for cooking, limiting its use to dressings and dips. This simply isn't true. The smoking point of olive oil varies depending on the type. Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO), for example, generally has a smoking point between 350°F and 410°F. While this might seem lower than some other oils, it's perfectly adequate for most cooking, as frying typically occurs between 350°F and 375°F.
This misconception often deters home cooks from using olive oil for sautéing or pan-frying, preventing them from enjoying its flavor and health benefits in cooked dishes. Even after extended frying, EVOO’s smoke point remains stable, highlighting its suitability for high-heat cooking. This stability is essential for preserving its nutritional value and flavor. Learn more about olive oil's smoke point here.
Understanding the Nuances of Olive Oil Varieties

The type of olive oil plays a significant role in determining its smoking point. Refined olive oil, unlike EVOO, undergoes processing that increases its smoking point. This makes it suitable for higher-heat cooking. However, refining can also remove some of the flavor and beneficial compounds found in EVOO. Choosing the right olive oil involves finding a balance between the desired cooking temperature and the desired flavor and nutritional profile. Email Marketing strategies can even incorporate information about olive oil varieties to engage customers interested in healthy cooking.
Olive Oil's Resilience in the Heat
Beyond the initial smoking point, the stability of an oil at high temperatures is also important. Olive oil, particularly EVOO, exhibits remarkable stability, meaning its smoking point doesn't dramatically decrease during prolonged heating. This characteristic makes it a reliable option even for longer cooking times.
Making Informed Choices in the Kitchen
Understanding olive oil's smoking point allows you to fully utilize this versatile ingredient. Don't hesitate to experiment! Use it for sautéing vegetables, pan-frying fish, or roasting chicken. By understanding the facts, you can unlock olive oil’s full culinary potential and enjoy its distinct flavor and health benefits.
Decoding Varieties: Not All Olive Oils Heat Equally
Olive oil is undeniably versatile in the kitchen. However, understanding the nuances of different varieties is key to maximizing its potential, especially regarding its smoking point. The production process significantly impacts an olive oil's performance under heat. Factors like acidity levels, filtration techniques, and even harvesting practices all influence the smoking point. This means not all olive oils are created equal when it comes to high temperatures.
Understanding the Spectrum of Olive Oils
The term "olive oil" encompasses a range of varieties, each with unique characteristics and ideal uses. Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) is considered the highest quality, boasting robust flavor and lower acidity. Virgin Olive Oil also comes from the first pressing but has a slightly higher acidity level, affecting its smoking point. Refined Olive Oil undergoes processing to remove impurities and increase its smoking point. However, this can diminish some flavor and nutritional benefits. This creates a direct relationship between olive oil type and its suitability for various cooking methods.
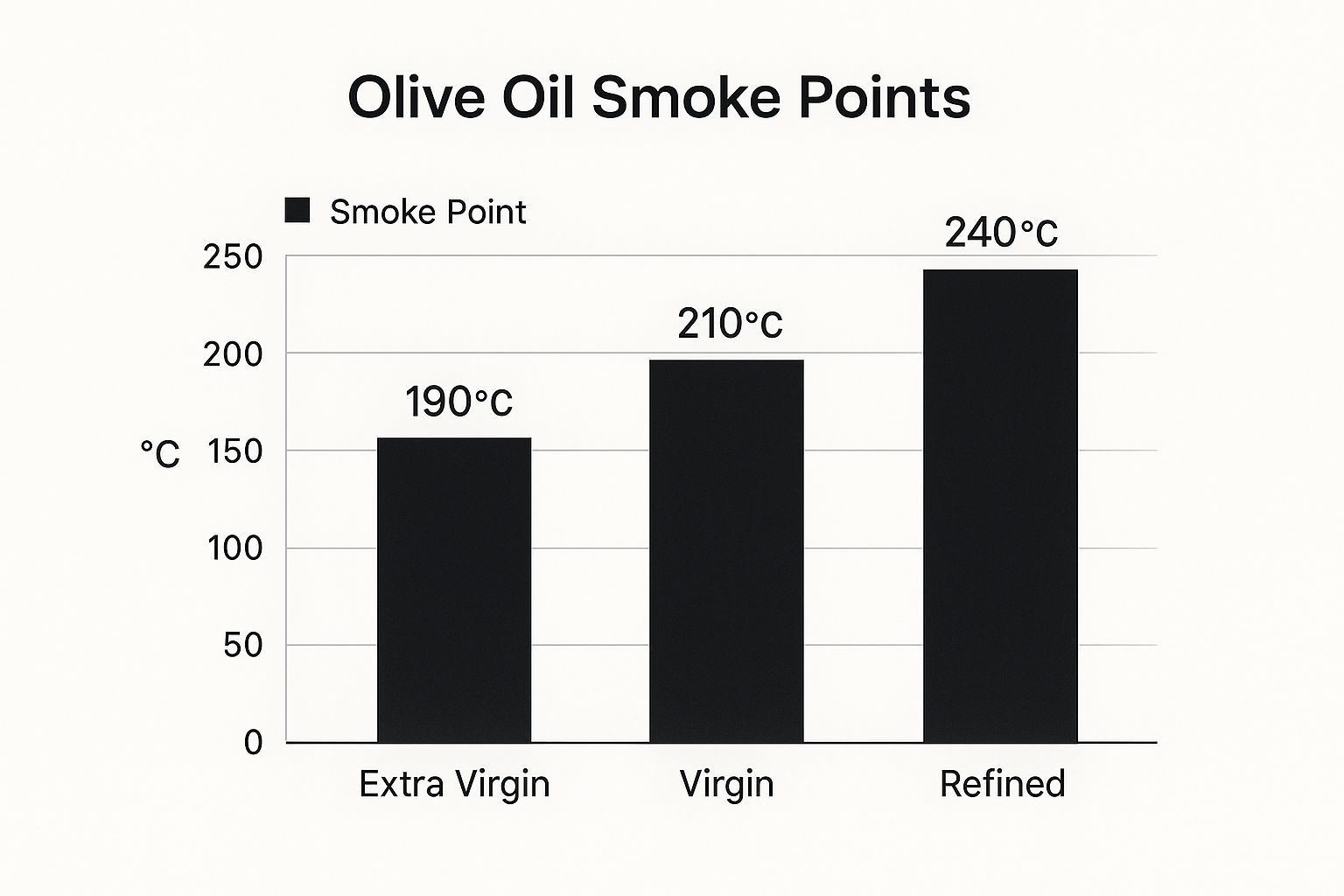
This infographic illustrates the varying smoke points of different olive oil types. As shown, Refined Olive Oil generally has the highest smoking point, followed by Virgin Olive Oil, with EVOO having the lowest. This visualization demonstrates how processing affects an oil's ability to withstand heat.
To further clarify the differences, let's examine a detailed comparison:
To help you choose the right olive oil for your cooking needs, we've compiled a handy table:
Olive Oil Types and Their Smoke Points
| Olive Oil Type | Smoke Point Range (°F) | Smoke Point Range (°C) | Best Cooking Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extra Virgin | 325-410 | 163-210 | Sauces, dressings, low-heat cooking |
| Virgin | 420-428 | 216-220 | Sautéing, baking |
| Refined | 465-470 | 241-243 | Frying, high-heat roasting |
This table summarizes the smoke points and best uses for each olive oil type. Remember, exceeding the smoke point can negatively impact the flavor and health benefits.
How Production Methods Impact Smoking Point
Acidity plays a crucial role in an olive oil's smoking point. Lower acidity, like in high-quality EVOO, contributes to a higher smoking point. Impurities in the oil, which contribute to acidity, burn more readily at lower temperatures.
Filtration also influences the smoking point. Unfiltered oils contain more sediment and particles, lowering the smoking point compared to filtered oils.
Finally, the olive harvest timing can subtly affect the oil's composition and, therefore, its smoking point. Olives harvested earlier may yield an oil with a slightly different chemical makeup than those harvested later, potentially impacting its performance under heat.
Choosing the Right Olive Oil for the Job
Selecting the correct olive oil for your cooking needs is paramount. For delicate tasks like sauces or dressings, where heat is minimal, EVOO's rich flavor is ideal.
However, for high-heat searing or frying, consider refined olive oil with a higher smoking point. By reading labels and understanding the different types, you can confidently choose the perfect one for any culinary endeavor. This knowledge empowers you to enhance the flavor and health benefits of your dishes.
Regional Variations and Traditional Practices
Olive oil production traditions vary significantly across regions. Some have even developed specific olive varieties optimized for distinct cooking applications.
For instance, certain robust varieties grown in parts of Spain are traditionally used for high-heat frying, reflecting centuries of culinary adaptation and understanding of olive oil's smoking point within regional cuisines. This highlights the deep connection between olive oil, culture, and cooking methods developed over generations. Understanding these traditions offers valuable insights into choosing the right olive oil.
Beyond the Smoke: Olive Oil Vs. Kitchen Competitors

Challenging common assumptions about cooking oils is essential to understanding olive oil's versatility. Many cooks prioritize a high smoke point, but this overlooks crucial factors. Oxidative stability, flavor preservation, and nutritional value under heat are where olive oil truly excels.
The Resilience of Olive Oil Under Heat
Some oils have high initial smoke points, but their performance degrades with prolonged heating. The temperature at which they start to smoke and break down lowers significantly during cooking. Olive oil, especially Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO), shows remarkable stability. Analyses reveal that while some oils may lose up to 150 degrees Fahrenheit from their smoke point over time, EVOO remains consistent. This makes it suitable even for deep frying, where sustained high heat is necessary. Olive oil's smoke point often equals or exceeds that of cottonseed and grapeseed oil, around 420°F. Learn more about olive oil smoke points. This highlights the importance of overall heat stability and taste, not just the initial smoke point.
Comparing Olive Oil to Other Cooking Oils
To understand olive oil's advantages, let's compare it with other popular cooking oils. We'll examine their smoke points, heat stability, how well they retain their flavor, and their ideal uses. This information will help you choose the right oil for different cooking methods.
To help illustrate these differences, we've compiled the following table:
Comparative Smoke Points of Popular Cooking Oils
| Oil Type | Smoke Point (°F) | Heat Stability | Flavor Retention | Best Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extra Virgin Olive Oil | 350-410 | High | Medium | Sautéing, Roasting, Baking, Dressings |
| Refined Olive Oil | 465-470 | High | Low | Frying, High-Heat Roasting |
| Canola Oil | 400 | Medium | Low | Baking, Stir-frying |
| Vegetable Oil | 400-450 | Medium | Low | General Cooking |
| Coconut Oil | 350 | Medium | Medium | Baking, Sautéing (Specific Applications) |
| Avocado Oil | 520 | High | Medium | High-Heat Cooking, Grilling |
This table reveals the trade-offs between various oils. While some have higher smoke points, they may compromise flavor and nutritional value at high heat. Olive oil, balancing heat stability and flavor, offers versatility for many cooking methods.
Choosing the Right Oil for Your Culinary Goals
The best oil isn't simply the one with the highest smoke point. Consider your culinary goals. Are you prioritizing flavor, nutritional content, or minimizing smoke? For delicate dishes where preserving ingredients is key, EVOO is excellent. For high-heat cooking, refined olive oil or avocado oil are better suited. Thinking about these factors empowers you to make informed decisions in the kitchen. Move beyond simple smoke point comparisons and choose the oil that best suits your needs.
From Ancient Kitchens to Modern Science
Olive oil's relationship with heat is a captivating blend of culinary history and scientific exploration. For thousands of years, Mediterranean cultures have incorporated olive oil into their high-heat cooking. This practice predates the scientific understanding of a smoking point. How did generations of cooks successfully navigate high-heat cooking with olive oil without this seemingly crucial information?
A Culinary Heritage of High-Heat Olive Oil
The answer is rooted in observation and experience. Ancient cooks recognized the subtle signs of an oil approaching its limit. These visual and olfactory cues, passed down through generations, guided their cooking techniques. This intuitive knowledge allowed them to maximize olive oil's benefits while minimizing any negative effects from heat. This connection between traditional practice and culinary expertise is profound.
The Rise of Scientific Scrutiny
The 20th century brought a shift toward scientific analysis. Researchers began defining the olive oil smoking point, aiming to set clear temperature boundaries for its use. However, this approach simplified a complex interaction, reducing the nuances of olive oil's behavior under heat to a single number. Early perceptions of olive oil's smoking point contributed to the misconception that it was unsuitable for high-heat cooking. This belief, prevalent in the early 2000s, has since been challenged. New research and practical culinary experience demonstrate that olive oil performs well at high temperatures, especially high-quality olive oil used correctly.
Some high-quality olive oils, like extra light olive oil, boast smoking points as high as 468°F, making them perfectly suitable for frying. The focus has also broadened beyond just the smoking point to encompass the oil's overall heat stability, an area where olive oil excels. Discover more insights about olive oil smoke points. This shift has increased olive oil’s popularity in kitchens worldwide, particularly in professional settings where both flavor and performance under heat are valued.
Bridging the Gap Between Tradition and Science
Today, we benefit from both scientific understanding and traditional knowledge. Modern science provides the tools to analyze the complexities of olive oil’s reaction to heat, while traditional practices offer invaluable context and proven techniques. Combining these perspectives unlocks olive oil’s full potential, enhancing our cooking and deepening our appreciation for its historical significance. Want to learn how to maximize your marketing ROI? Explore methods to boost your marketing ROI.
Rediscovering Ancient Wisdom
Modern research often validates what generations of cooks already knew. High-quality extra virgin olive oil exhibits remarkable heat stability, meaning its smoking point remains relatively consistent during cooking. This makes it a reliable choice even for high-heat applications. The scientific journey of olive oil has, in many ways, brought us full circle, reaffirming the wisdom of ancient culinary traditions.
Master Techniques: Unlocking Olive Oil's Full Potential

Olive oil is a kitchen staple, but are you truly harnessing its full potential? Understanding how this versatile oil behaves under heat can transform your cooking. This section explores professional techniques for temperature control, oil quantity management, and cookware selection to help you make the most of olive oil.
Temperature Control: The Key to Success
Controlling the temperature is paramount when cooking with olive oil. Overheating can cause the oil to reach its smoking point. This not only degrades the oil's quality and flavor, imparting a burnt taste, but also diminishes its health benefits. A good rule of thumb is to keep the temperature below 400°F for most cooking applications. For instance, when sautéing vegetables, use medium heat to prevent the olive oil from overheating. This allows the oil to enhance the dish without compromising its delicate flavor.
Managing Olive Oil Quantity
The amount of olive oil used plays a significant role in its performance under heat. Using too much oil can result in uneven cooking and increase the likelihood of reaching the smoking point. Conversely, using too little can lead to sticking and burning. Finding the right balance is essential. Start with a moderate amount, similar to how you would season a griddle, and add more only if needed. This allows for greater control over the cooking process and ensures your food cooks evenly.
Choosing the Right Cooking Vessels
Your cookware's material and construction significantly influence how olive oil heats and performs. Materials like stainless steel and cast iron provide even heat distribution, promoting consistent cooking. A pan with a heavy bottom helps prevent hot spots and maintains a more stable temperature, which is especially important when searing or frying with olive oil. This stability allows for greater precision and control.
Specific Techniques for Different Cooking Applications
Different cooking methods benefit from specific techniques to maximize olive oil's attributes.
- Searing: Use a high-quality extra virgin olive oil with a higher smoking point. Make sure the pan is hot before adding the food to achieve a perfect sear.
- Frying: Opt for refined olive oil, which has a higher smoking point than extra virgin, making it better suited for frying. Carefully monitor the temperature to prevent overheating.
- Roasting: Extra virgin olive oil imparts wonderful flavor to roasted vegetables and meats. Toss the food with a moderate amount of olive oil before roasting.
Combining Olive Oil with Other Ingredients
Combining olive oil with other ingredients can create a more stable cooking environment. For example, adding a small amount of butter to olive oil when sautéing can raise the smoking point of the mixture. Incorporating herbs and spices not only enhances flavor but can also contribute to a more balanced cooking process.
Troubleshooting and Visual Indicators
Recognizing when olive oil is nearing its smoking point is crucial. If you see wisps of smoke or the oil shimmers excessively, immediately reduce the heat. This prevents the oil from breaking down and preserves its flavor. A burnt smell is another indicator of overheating. By mastering these techniques and observing visual cues, you can unlock the full potential of olive oil and elevate your culinary skills. Experimentation and observation will enhance your understanding of this versatile ingredient.
The Health Equation: Heat, Olive Oil, and Nutrition
Olive oil is a staple in many kitchens, prized for its flavor and potential health benefits. But a common question arises: how does heat affect these advantages? Let's explore the intricate relationship between cooking temperatures and olive oil's nutritional value.
Heat's Impact on Bioactive Compounds
Olive oil boasts bioactive compounds, such as polyphenols, which contribute significantly to its health-promoting properties. Heating olive oil can modify these compounds, leading to concerns about whether high-temperature cooking diminishes its nutritional value. However, it's important to note that these compounds don't all react to heat uniformly.
Some polyphenols exhibit impressive heat stability, remaining intact even after prolonged exposure to high temperatures. Others are more delicate and may degrade with excessive heat. Therefore, choosing the right olive oil and using appropriate cooking methods is key to preserving its beneficial properties.
The Formation of Potentially Harmful Compounds
Another concern revolves around the formation of potentially harmful compounds when heating olive oil. While all oils undergo changes at high temperatures, olive oil holds up relatively well. Its high monounsaturated fat content contributes to its stability, making it less susceptible to oxidation than oils rich in polyunsaturated fats. This relative stability is a crucial factor when considering olive oil's healthfulness in different cooking scenarios.
Challenging Outdated Nutritional Guidelines
Previous dietary guidelines often cautioned against using olive oil for high-heat cooking. However, recent research challenges these long-held beliefs. Studies indicate that high-quality olive oil, such as extra virgin olive oil, remains remarkably stable even at temperatures typically used for frying. This suggests that earlier recommendations may have unnecessarily restricted the use of this versatile and valuable ingredient. These findings encourage a re-evaluation of conventional wisdom and a broader acceptance of olive oil in various cooking applications.
Practical Temperature Thresholds for Health and Flavor
Optimizing both culinary enjoyment and health benefits involves understanding practical temperature thresholds. While specific limits depend on the olive oil variety and cooking method, a general guideline is to keep temperatures below 400°F for most uses. This temperature range allows for the development of desirable flavors while minimizing the risk of nutrient degradation.
Ultimately, making informed choices about olive oil and heat doesn't necessitate overly restrictive practices. Selecting high-quality extra virgin olive oils and utilizing appropriate cooking methods can maximize both flavor and health benefits.
Ready to delve deeper into the world of olive oil? Visit Learn Olive Oil to explore everything from choosing the best varieties to mastering various culinary techniques.

Leave a comment