Why Proper Olive Oil Storage Makes or Breaks Quality
That beautiful bottle of olive oil you carefully selected isn't just a cooking ingredient; it's a source of flavor and potential health benefits. However, the compounds that make olive oil so special, like polyphenols and antioxidants, are fragile. Proper storage isn't just about avoiding waste; it's about preserving the vibrant aromas, flavors, and health benefits that make olive oil worthwhile.
The Science Behind Olive Oil Degradation
Olive oil degrades primarily due to oxidation, a chemical reaction triggered by light, oxygen, and heat. This process breaks down the beneficial compounds, leading to off-flavors and rancidity. Think of an apple browning after being cut – a similar process occurs with olive oil.
Exposure to light, especially UV rays, accelerates oxidation. Oxygen also interacts with the oil's molecules, impacting its flavor. Heat further magnifies the damage caused by light and oxygen. Storing olive oil near the stove or a sunny windowsill is detrimental to its quality.
Scientific studies confirm the damaging effects of light and oxygen. A three-year Australian study demonstrated that extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) stored in clear bottles exposed to light and air lost up to 40% of its polyphenols and became rancid up to five times faster than oil stored in tinted glass in dark, cool conditions. Even short-term light exposure (less than a week) can downgrade EVOO quality according to International Olive Council standards.
This research explains why leading olive oil producers and retailers (representing over 70% of premium EVOO sales) now use opaque or dark glass and recommend cool, dark storage away from heat. Learn more about olive oil storage conditions
The Consequences of Improper Storage
Improper storage does more than just diminish flavor. Oxidation reduces nutritional value by destroying antioxidants. Rancid olive oil also develops unpleasant tastes and smells, making it unappetizing and potentially harmful.
Neglecting proper storage can turn premium EVOO into a subpar cooking oil, or worse, something you have to discard, within months. Protecting your investment in high-quality olive oil means understanding the factors that impact its lifespan and using the right storage techniques.
Finding the Perfect Temperature for Olive Oil Longevity

Maintaining your olive oil's quality goes beyond simply shielding it from light and air. Temperature plays a vital role in preserving its delicate flavor, aroma, and beneficial properties. Proper storage can significantly extend its shelf life, ensuring you enjoy its full potential. This involves understanding the ideal temperature range and the impact of temperature fluctuations.
The Ideal Temperature Sweet Spot
The ideal temperature for storing olive oil falls between 57°F (14°C) and 70°F (21°C). This optimal range prevents rapid degradation while also avoiding unwanted changes in texture or flavor. It’s similar to storing fresh produce: too warm and it spoils, too cold and it can suffer damage.
Storing olive oil above your stove, even in a seemingly protected cabinet, exposes it to temperature spikes from cooking. These fluctuations accelerate oxidation, causing your olive oil to become rancid much faster. Even short bursts of heat can degrade its quality.
Seasonal Considerations for Olive Oil Storage
Just as you adjust your wardrobe with the seasons, consider adapting your olive oil storage. In warmer months, keep it away from windows or areas with direct sunlight. During colder months, prevent solidification by storing it in a consistently cool, but not freezing, spot.
Refrigeration: Does It Harm Olive Oil?
Refrigerating certain olive oils, particularly robust varieties, can cause them to solidify and turn cloudy. This is a temporary, cosmetic change and doesn't inherently harm the oil. It returns to normal at room temperature. However, consistent temperature is key, so avoid frequent temperature shifts.
To help illustrate the best temperature ranges and their effects, let's look at the following table:
Olive Oil Storage Temperature Guidelines
This table presents optimal temperature ranges for olive oil storage and their effects on oil quality over time.
| Temperature Range | Effect on Quality | Expected Shelf Life | Recommended For |
|---|---|---|---|
| 57°F (14°C) – 70°F (21°C) | Optimal; preserves flavor and aroma | 18-24 months | All olive oil types |
| Above 70°F (21°C) | Increased oxidation, flavor degradation | Less than 18 months | Not recommended |
| Below 57°F (14°C) but above freezing | Solidification, cloudiness (reversible) | 18-24 months | Robust olive oils; avoid frequent temperature changes |
| Below freezing | Not recommended; may permanently alter properties | N/A | Not recommended |
This table clearly demonstrates the importance of keeping your olive oil within the ideal temperature range. While slight variations may not be catastrophic, consistently high temperatures significantly shorten shelf life and negatively impact quality.
Research over the last decade underscores the importance of storage temperature for olive oil. Studies show that Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) stored at lower temperatures (between +4°C and −20°C) maintains quality better than room temperature storage. One study found that EVOO stored at these lower temperatures for 12 months experienced only slight (5-10%) decreases in phenolic content, with volatile compounds remaining largely stable. However, room temperature storage led to significant oxidation and faster quality decline, especially after 3-6 months. This is particularly relevant as approximately 85% of EVOO is purchased from supermarkets with suboptimal storage.
Practical Storage Solutions
Finding the right storage spot can be tricky, especially in smaller kitchens. Consider a temperature-controlled pantry, or if space is limited, a cool, dark cupboard away from heat sources. Even a drawer or shelf in a less-used kitchen area can create a suitable environment. The goal is a stable, cool temperature to protect your olive oil and enjoy its full flavor and benefits.
Selecting the Ultimate Olive Oil Container

Choosing the right container for your olive oil is just as important as finding the ideal storage temperature. The container acts as a barrier against light and oxygen, two key factors that can degrade the quality of your olive oil. Selecting the correct vessel can significantly impact the lifespan and flavor of your oil.
Material Matters: Choosing the Right Material
The container material directly affects its ability to protect the olive oil. Dark glass is a popular choice, effectively blocking light, a major contributor to oxidation. However, dark glass isn't airtight, so oxygen exposure still occurs, leading to gradual degradation over time.
Tin-plated steel is another option, frequently used for larger storage containers. It offers decent light protection. However, the headspace within these containers can introduce oxygen to the oil. Additionally, while durable, metal can affect the flavor profile over time. For example, one study found that tin-plated steel preserved olive oil quality for about 80 days at room temperature, while bag-in-box containers extended that to 120 days.
Bag-in-box containers are increasingly recognized as a superior storage method. Their airtight, collapsible design minimizes oxygen exposure and effectively blocks light. This leads to exceptional preservation, keeping extra virgin olive oil fresh for up to 120 days at room temperature and 100 days at higher temperatures.
Size and Closure: Optimizing for Freshness
Container size and closure type also play a role in preserving olive oil quality. Smaller containers are generally preferred because they reduce the amount of air the oil is exposed to after opening. Similar to a half-full soda bottle going flat quicker than a nearly full one, every time you open a container, you introduce more oxygen, accelerating degradation.
A secure, airtight seal is essential. Screw-on caps and corks are common, but don't always provide a perfect seal. Bag-in-box systems stand out in this aspect. Their collapsible design naturally expels excess air, minimizing oxidation.
Pour Spouts and Aesthetics: Balancing Form and Function
While elegant pour spouts can enhance your kitchen's appearance, consider their effect on your olive oil. Some spouts can introduce air, counteracting other preservation efforts. Choose spouts that minimize air exposure, or opt for simple, airtight closures.
Ultimately, the best olive oil container depends on your individual needs. If you use olive oil regularly, dark glass bottles are convenient and visually appealing for short-term storage. For larger quantities or infrequent use, bag-in-box containers offer superior protection against light and oxygen, significantly extending shelf life. By making informed decisions based on your usage, you can ensure your olive oil retains its quality and flavor.
Where to Store Your Olive Oil for Maximum Freshness

Finding the right spot to store your olive oil is crucial for maintaining its quality. While some locations might seem suitable, they could be harming your oil without you even realizing it. This section explores the best storage practices and techniques for different kitchen layouts, helping you keep your olive oil fresh and flavorful.
Identifying Ideal Storage Spots
The golden rule for olive oil storage is "cool, dark, and dry." However, putting this rule into practice in your kitchen requires a bit more thought. For example, a pantry might seem like a good option, but how close is it to your oven or direct sunlight? Even slightly warmer temperatures can cause oxidation, reducing the oil's quality.
When choosing a container, consider options like sustainable takeout packaging. You can also repurpose existing kitchen storage. A cool, dark drawer, a cabinet away from the stove, or a shelf in a cooler part of your kitchen can all work well.
Creative Solutions for Challenging Kitchens
Small kitchens or apartments with limited space call for innovative storage solutions. If counter space is limited, create an "olive oil station" inside a cabinet or pantry. This could be a small tray or basket to keep your bottles organized and away from heat and light.
If your kitchen has a lot of natural light, opt for darker cabinets or use opaque containers to block UV rays. For homes with minimal cabinet space, wall-mounted shelves in a cooler area can create a dedicated and easy-to-access storage spot.
Seasonal Adjustments: Adapting to Temperature Changes
Professional chefs often change their olive oil storage strategies with the seasons. During summer, they might move their olive oil to a cooler basement or cellar. In winter, they avoid storing it near exterior walls to protect it from temperature swings. This proactive approach ensures consistent quality throughout the year.
Limited storage space and competing needs often require creative solutions. Using vertical space with stackable containers or adding small shelves inside cabinets can help maximize efficiency. These simple adjustments can protect your investment in quality olive oil and help it last longer.
Professional Tips for Maintaining Oil Quality
Culinary professionals use specific techniques to keep olive oil fresh. They minimize headspace by transferring oil from larger containers to smaller bottles as needed, reducing exposure to oxygen. They also use airtight containers to further prevent oxidation. These small steps can significantly extend the oil's shelf life and preserve its delicate flavor.
How Your Olive Oil Variety Demands Different Care
Not all olive oils are created equal. Just as a delicate Pinot Noir requires different handling than a robust Cabernet Sauvignon, your olive oil needs specific care depending on its variety. A delicate Arbequina, for example, reacts differently to environmental factors than a robust Koroneiki. Understanding these differences is key to preserving your olive oil's quality and flavor.
Chemical Composition and Shelf Stability
The chemical composition of olive oil, particularly its polyphenol and antioxidant content, plays a vital role in its shelf life. These compounds act as natural preservatives, protecting against oxidation. Different olive varieties, however, contain varying levels of these protective elements. Picual olives are known for their high polyphenol content, contributing to a longer shelf life. Arbequina olives, with their milder flavor, typically have fewer polyphenols. This makes Arbequina olive oil more susceptible to oxidation and requires more careful storage.
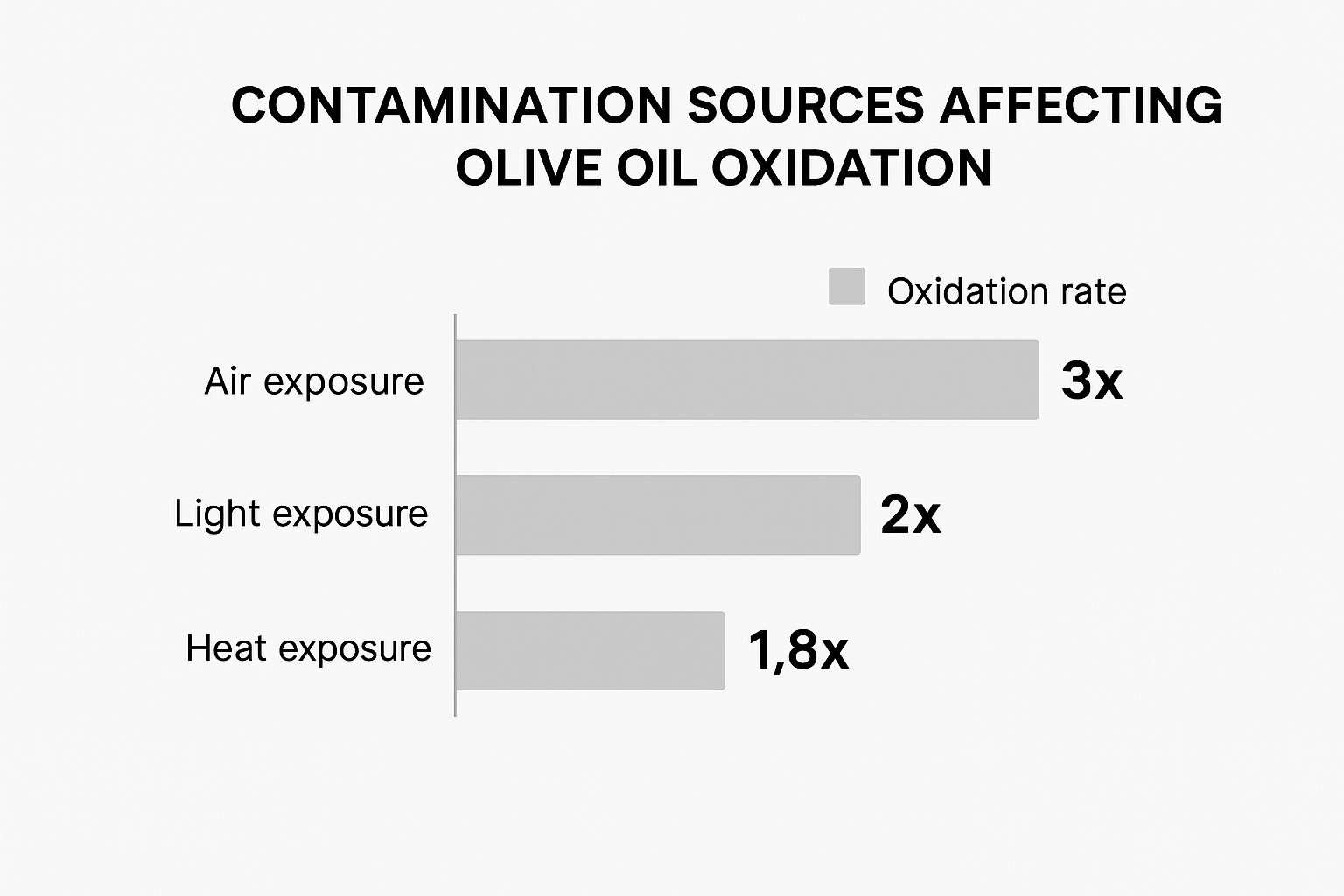
The infographic above illustrates how air, light, and heat contribute to olive oil oxidation. Air exposure has the most significant impact, accelerating oxidation by three times. Light exposure doubles the oxidation rate, and heat increases it by 1.8 times. Minimizing exposure to these elements is crucial, especially for delicate varieties.
Regional Variations and Natural Resistance
The climate and terroir where the olives are grown influence an oil's resilience. Oils from some regions naturally have higher antioxidant levels, enhancing their stability. For example, olive oils from certain areas of Greece, with their harsh sun and dry climate, often show greater oxidation resistance.
Storage duration and the specific olive cultivar also significantly influence quality degradation. A 2024 study found that some Italian cultivars, like Bianchera and Caninese, showed over a 50% increase in oxidation markers after seven months of storage. Others, like Leccino, Moraiolo, and Pendolino, showed less than a 20% increase. These findings underscore that not all olive oils age the same. Cultivar selection significantly impacts storage outcomes. Discover more insights about olive oil storage.
Practical Adaptation Strategies: Tailoring Your Approach
Understanding your olive oil's characteristics lets you implement the best storage practices. For delicate, low-polyphenol oils, extra precautions are necessary. Use smaller, airtight containers to minimize oxygen exposure and store them in a consistently cool, dark place.
For robust, high-polyphenol varieties, a slightly less stringent approach is acceptable. While they still benefit from proper storage, they are less susceptible to rapid degradation.
The following table provides a quick overview of storage recommendations for various olive oil types:
Olive Oil Variety Storage Comparison
This table compares different olive oil varieties and their storage characteristics, including shelf life and sensitivity to environmental factors.
| Olive Oil Variety | Oxidation Resistance | Recommended Storage Method | Typical Shelf Life |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arbequina | Lower | Cool, dark place, airtight container | 12-18 months |
| Picual | Higher | Cool, dark place, airtight container | 18-24 months |
| Koroneiki | Medium | Cool, dark place, airtight container | 18 months |
| Delicate Oils (e.g., Tuscan) | Lower | Cool, dark place, small airtight container | 12-18 months |
| Robust Oils (e.g., some Greek varieties) | Higher | Cool, dark place, airtight container | 18-24 months |
This table highlights the importance of tailoring storage methods to specific olive oil varieties. Delicate oils, like Arbequina and Tuscan varieties, require more stringent storage due to their lower oxidation resistance. Robust oils, like Picual and some Greek varieties, have a longer shelf life and greater tolerance for less-than-ideal storage conditions. However, all olive oils benefit from being stored in a cool, dark place in an airtight container.
By recognizing the individual needs of each variety, from peppery Tuscan oils to buttery California blends, you preserve the unique flavor profile and maximize the shelf life of your olive oil. Pay attention to the label information and tailor your storage methods accordingly.
Olive Oil Storage Blunders That Ruin Your Investment
Storing olive oil might seem straightforward, but surprisingly common mistakes can dramatically impact its quality. Let's explore some of these blunders and understand how they affect your precious olive oil. These errors can transform your premium extra virgin olive oil into a subpar cooking oil, or worse, something unusable.
The Enemy of Flavor: Light, Heat, and Air
The three primary threats to olive oil are light, heat, and air. Storing your olive oil in a clear container on a sunny windowsill or near the stove is a surefire way to compromise its quality. Light, particularly UV rays, accelerates oxidation, breaking down the beneficial compounds and diminishing the flavor. Heat intensifies this damage. Every time you open a bottle, you introduce oxygen, further contributing to degradation. This hastens rancidity, resulting in an unpleasant taste and smell.
- Storing near the stove: While convenient, the heat from cooking, even residual warmth, significantly degrades the oil.
- Using clear containers: Clear glass bottles may look appealing, but they allow harmful UV rays to penetrate. Opt for dark-colored or opaque containers that offer protection from light.
- Leaving containers open: Similar to how a cut apple browns in the air, olive oil oxidizes with exposure to oxygen. Ensure bottles are tightly sealed after each use.
- Ignoring temperature fluctuations: Even small temperature changes, like those near a frequently used oven, can negatively affect the oil’s delicate flavor profile.
- Using large containers for small amounts of oil: The more headspace (air) in the container, the faster the oil degrades. Use smaller bottles or transfer oil from larger containers to smaller ones as you use it.
Recognizing the Signs of Spoilage
Identifying compromised olive oil is crucial for salvaging what you can and avoiding culinary disappointments. Here are some key indicators:
- Rancid Smell: Fresh olive oil has a pleasant, fruity aroma. Rancid oil develops a musty, sour, or even crayon-like smell.
- Off-Flavor: If the characteristic peppery bite has transformed into a harsh, unpleasant taste, it's a sign of oxidation.
- Cloudy Appearance: While some temporary cloudiness can occur in cold temperatures, persistent cloudiness at room temperature might indicate spoilage.
- Muddy Sediment: A small amount of sediment is normal, but excessive or unusually dark sediment is a warning sign.
Rescue and Recovery: Saving Your Olive Oil
If you detect the problem early, you might be able to salvage some of the oil. Transfer it to a smaller, airtight, opaque container and store it in a cool, dark location. Use it quickly. For temperature-shocked oil, allow it to return to room temperature slowly in a cool, dark area. However, if the oil is significantly rancid, it’s best to discard it.
By avoiding these common storage mistakes and recognizing the early signs of spoilage, you can protect your investment in high-quality olive oil. Proper storage is essential for preserving the flavor, aroma, and nutritional benefits. Learn more about selecting the perfect olive oil on learnoliveoil.com
Detecting When Your Olive Oil Has Gone Bad
Developing a discerning palate for olive oil isn't just for connoisseurs. Understanding how to identify when your olive oil has turned rancid protects your investment and ensures you're using the best quality oil in your dishes. This guide will lead you through sensory explorations and simple tests to help you become a confident olive oil expert.
Sensory Evaluation: Engaging Your Senses
Much like appreciating a fine wine, evaluating olive oil involves engaging your senses. But instead of searching for notes of fruit or oak, you'll be focusing on indicators of freshness and decay.
-
Aroma: Fresh, high-quality olive oil boasts a pleasant, often fruity aroma. Common descriptors include grassy, herbaceous, or even a subtle peppery scent. Rancid oil, however, has a distinctly unpleasant odor that can be musty, sour, or even reminiscent of crayons. This off-putting smell signals oxidation.
-
Taste: The hallmark peppery bite you feel at the back of your throat when tasting fresh olive oil is a sign of its quality. If this peppery sensation is replaced by a harsh, bitter, or metallic taste, the oil has likely oxidized.
-
Appearance: While not always a definitive indicator, a cloudy or hazy appearance at room temperature can sometimes point towards spoilage. Some cloudiness is normal when olive oil is stored at cooler temperatures and should dissipate as it warms.
Home Tests: Unveiling Hidden Deterioration
In addition to your senses, a few simple home tests can uncover hidden deterioration.
-
The "Float Test": This test can offer clues, although it's not foolproof. Pour a small quantity of olive oil into a glass of water. If the oil floats as a cohesive layer on the surface, it’s likely still good. If it disperses into droplets or sinks, degradation may be starting.
-
The "Smell Test" After Heating: Gently warm a small amount of olive oil in a pan. Heat amplifies existing aromas. If you detect unpleasant smells that weren't apparent at room temperature, oxidation has likely begun.
Salvaging or Discarding: Making the Right Decision
Slightly compromised olive oil can sometimes be salvaged. If you notice early signs of deterioration, transfer the oil to a smaller, airtight, opaque container. Store it in a cool, dark environment and use it quickly for cooking, where subtle off-flavors may be less noticeable. If the oil is significantly rancid, however, it's best to discard it.
By honing your sensory awareness and employing these simple tests, you can confidently judge the quality of your olive oil. Distinguishing between the vibrant peppery kick of fresh oil and the acrid sting of rancidity allows you to maximize the culinary potential of every drop. Learn more at Learn Olive Oil.

Leave a comment