Is Your Olive Oil the Real Deal?
Want to know how to tell if olive oil is real? Counterfeit olive oils are a common problem, affecting both taste and health. This list provides 7 simple ways to check your olive oil's authenticity, ranging from quick at-home tests to professional analysis. Learn how to identify fake olive oil and enjoy the genuine flavor and health benefits of real extra virgin olive oil. From the cold test to label analysis, these checks help ensure you're getting what you paid for.
1. Cold Test (Refrigeration Method)
One of the simplest ways to tell if olive oil is real is the cold test, also known as the refrigeration method. This test leverages the scientific principle that different types of fats solidify at different temperatures. Genuine extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is high in monounsaturated fats, which tend to solidify at cooler temperatures than other oils often used as adulterants. By refrigerating your olive oil, you can observe its reaction to cold and gain clues about its purity. This method is particularly useful as a preliminary test because it requires no special equipment and can be done at home with just your refrigerator and a small amount of oil.
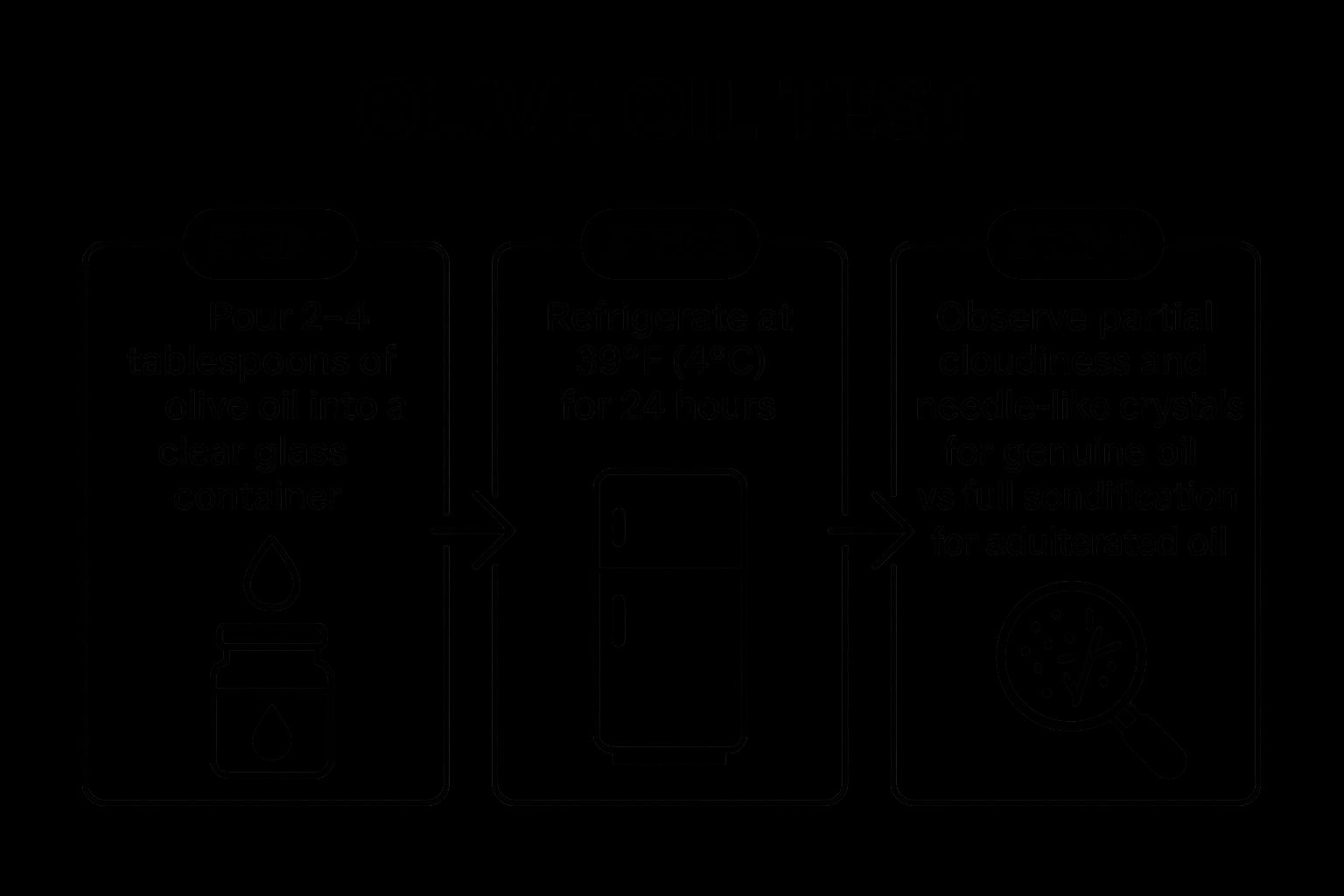
The infographic below details the process of conducting the cold test at home. It outlines the steps involved in refrigerating and observing your olive oil for signs of solidification.

As the infographic demonstrates, real EVOO will typically become cloudy and partially solidify, often forming needle-like crystals, while fake olive oil, potentially mixed with other oils like canola or vegetable oil, may solidify completely or remain unchanged. The change in texture and the formation of crystals, or lack thereof, give you a visual indication of the oil's authenticity.
This method deserves its place on this list due to its accessibility and simplicity. It's a cost-effective way to get a quick indication of your olive oil's quality. While not foolproof, it can be a helpful first step before considering more expensive or complex testing methods. Studies by UC Davis researchers and recommendations by Consumer Reports further validate the use of the cold test as a preliminary assessment tool for detecting fraudulent olive oil.
Pros:
- Accessible for home testing
- No cost beyond the oil itself
- Non-destructive to the oil sample
Cons:
- Not 100% conclusive as some adulterated oils can mimic genuine solidification patterns
- Results can be subjective and difficult to interpret for beginners
- Some high-quality oils may not solidify as expected due to varietal differences
Tips for Conducting the Cold Test:
- Place 2-4 tablespoons of olive oil in a clear glass container.
- Refrigerate for 24 hours.
- Observe for cloudiness and partial solidification. Authentic EVOO will typically form needle-like crystals or a partially solid mass. If it becomes completely solid, it may indicate adulteration.
- Allow the oil to return to room temperature. Genuine olive oil should return to its clear liquid state.
For a visual demonstration of the cold test, you can watch this video:
By following these steps, you can use the cold test to gain valuable insights into the authenticity of your olive oil, helping you ensure you are purchasing and consuming a high-quality product. This simple method can empower you to make informed choices when selecting olive oil, benefiting your health and culinary experiences.
2. Sensory Evaluation (Taste and Smell Test)
One of the most effective ways to tell if your olive oil is real is through sensory evaluation—a taste and smell test. This method, championed by experts and organizations like the International Olive Council (IOC), mimics the process used by professional olive oil tasters to discern authentic extra virgin olive oil. It relies on developing your senses of smell and taste to identify the key characteristics of genuine olive oil, focusing on specific positive and negative attributes. Real extra virgin olive oil should exhibit a combination of fruity, bitter, and pungent notes, with no defects present.

This method deserves a place on this list because it gets to the heart of what defines high-quality olive oil. It's the official method used by certified olive oil tasting panels worldwide, including those of the California Olive Oil Council (COOC) and the NYIOOC World Olive Oil Competition, highlighting its importance in the industry. The sensory evaluation process examines the oil for three primary positive attributes: fruitiness, referring to the aroma and flavor of fresh olives; bitterness, a desirable quality found primarily on the tongue; and pungency, a peppery sensation felt in the back of the throat, often linked to the presence of the beneficial compound oleocanthal. Crucially, it also checks for defects. These negative attributes, including rancidity (a stale, oily flavor), fustiness (a damp, musty smell), and mustiness (a flavor reminiscent of mold or damp earth), are clear indicators of a low-quality or adulterated oil. If any of these defects are detected, the oil is likely not real extra virgin olive oil.
How to Conduct Your Own Sensory Evaluation:
- Warm the oil: Pour a small amount of olive oil into a small glass. Cup the glass in your hands to gently warm the oil and release its aromas.
- Smell the oil: Swirl the oil in the glass and inhale deeply. Authentic extra virgin olive oil should have a fresh, fragrant aroma, often described as grassy, fruity (like ripe or green olives), and sometimes peppery. Any off-odors, like those described above, are warning signs.
- Taste the oil: Take a small sip of the oil and let it coat your tongue. Note the flavors – is it fruity, bitter, and pungent? Pay attention to the back of your throat for a peppery sensation. This "throat catch" is a good indicator of the presence of oleocanthal, a potent antioxidant.
Pros and Cons of Sensory Evaluation:
Pros:
- No special equipment: All you need are your senses.
- Immediate results: You can assess the quality quickly.
- IOC-recognized: This is an official and respected method.
- Effective when trained: For experts, it is a highly accurate assessment tool.
Cons:
- Requires training: Distinguishing subtle flavors and defects takes practice.
- Subjective: Personal preferences can influence perceptions.
- Difficult for beginners: Novice tasters may struggle to identify specific defects.
Tips for Improving Your Sensory Skills:
- Practice regularly: Taste known high-quality extra virgin olive oils to develop your sensory memory.
- Comparative tasting: Sample several different oils side-by-side to better discern their unique characteristics.
- Start simple: Focus on identifying the basic positive attributes (fruitiness, bitterness, pungency) and common defects (rancidity, mustiness) before attempting more nuanced evaluations.
By understanding and practicing sensory evaluation, you can significantly improve your ability to how to tell if olive oil is real and select high-quality extra virgin olive oils. This empowers you to make informed choices and fully enjoy the numerous health benefits and culinary delights that real extra virgin olive oil has to offer.
3. UV Light/Fluorescence Testing
One intriguing method to help determine if your olive oil is truly extra virgin is through UV light/fluorescence testing. This technique leverages the natural fluorescence of compounds within the oil, primarily chlorophyll, to provide clues about its authenticity. When exposed to a UV light, pure extra virgin olive oil will typically exhibit a yellowish-green glow due to the presence of chlorophyll. Conversely, refined or adulterated oils, often lacking these natural compounds, may fluoresce with a different color, often a dull blue. This difference in fluorescence can be a valuable tool in your quest to ascertain whether the olive oil you're purchasing is the real deal.

This test relies on the principle that different compounds absorb and emit light at varying wavelengths. Chlorophyll and other naturally occurring components in extra virgin olive oil absorb UV light and re-emit it as a yellowish-green fluorescence. Refined oils, having undergone processes that strip away these natural components, will often display a different fluorescence. This test offers a relatively quick and visual method to potentially differentiate between extra virgin and other types of olive oil. This method deserves its place on this list because it offers a relatively accessible and affordable way to gain further insight into olive oil authenticity, especially when combined with other testing methods.
This method is particularly useful for consumers wanting a preliminary at-home check to help determine if their olive oil is real. While not definitive proof, it can raise red flags if the fluorescence doesn't align with what's expected of extra virgin olive oil. For example, some Italian food fraud investigations have employed spectrofluorimetry, a more sophisticated version of this test, to uncover adulterated olive oil. Some olive oil producers even use fluorescence as a preliminary quality control check during production.
Pros:
- Relatively simple to perform at home.
- Low cost once you have a UV light (a blacklight around 365nm wavelength is recommended).
- Provides quick results without destroying the sample.
- Visual evidence is easy to interpret.
Cons:
- Not completely conclusive, as some adulterants can mask the true fluorescence.
- Limited scientific validation for home testing scenarios.
- UV exposure may potentially affect oil quality if exposed for an extended period.
- Results can vary based on olive variety, harvest date, and production method.
Tips for UV Light/Fluorescence Testing:
- Use a dark room for optimal visibility of the fluorescence.
- Place the olive oil in a clear glass container for testing.
- Compare the suspected oil against a known authentic extra virgin olive oil sample.
- Remember, pure EVOO should show a yellowish-green fluorescence, not a bright blue.
- Take photos to document and compare results over time.
By understanding the nuances of UV light/fluorescence testing and following these tips, you can use this technique as one piece of the puzzle in determining if your olive oil is genuinely extra virgin. While not foolproof on its own, it can contribute valuable information in your quest for how to tell if olive oil is real.
4. Oil Lamp Test
This ancient method, also known as the lamp test, offers a rudimentary way to assess the purity of your olive oil. If you're wondering how to tell if olive oil is real, this test, rooted in historical practices, might pique your interest. It leverages the principle that pure olive oil burns differently than adulterated oils due to its unique chemical composition. For thousands of years, long before electricity, olive oil was a primary source of light. This widespread use led to the observation that pure olive oil burned cleanly and steadily in lamps, while impure oils exhibited different burning characteristics.
How it Works:
The oil lamp test relies on the combustion properties of different oils. Pure olive oil has a specific fatty acid profile that allows it to burn cleanly and consistently with a clear, bright flame. Conversely, oils mixed with impurities or other cheaper oils tend to produce more smoke, flicker irregularly, sputter, or emit unusual odors when burned.
Features:
- Based on the unique combustion properties of olive oil.
- Requires only a simple oil lamp or a DIY setup (e.g., a small ceramic dish with a cotton wick).
- Evaluates smoke production, flame behavior (steady vs. flickering), and burning odor.
Pros:
- Historical Significance: This test is grounded in traditional olive oil authentication practices, offering a glimpse into how purity was assessed in the past.
- Simplicity: It's easy to perform and requires minimal equipment.
- Immediate Visual Feedback: The results are readily observable.
Cons:
- Destructive Test: This method consumes a portion of your olive oil sample.
- Fire Safety Concerns: Open flames require careful handling and proper ventilation.
- Limited Reliability: Less reliable than modern analytical methods, as some adulterants may burn similarly to pure olive oil. It cannot definitively determine purity or identify specific adulterants.
- Lacks Scientific Precision: It's a subjective observation rather than a quantifiable measurement.
Examples:
Historically, the oil lamp test was used throughout the Mediterranean region, especially in areas like Greece and Italy, to assess olive oil quality. Even today, it's occasionally demonstrated at traditional olive oil festivals in these countries.
Tips for Performing the Oil Lamp Test:
- Use a small, shallow ceramic dish and a cotton wick.
- Ensure the area is well-ventilated and take necessary fire safety precautions.
- Compare the burning characteristics of your olive oil sample with a known authentic sample for reference.
- Pure olive oil should burn with a clear, steady flame, minimal smoke, and no unpleasant or rancid odors.
- Observe whether the oil sustains a consistent flame or flickers and sputters.
Why This Test Deserves Its Place on the List:
While not a definitive test for purity in today's world, the oil lamp test offers a fascinating historical perspective on how to tell if olive oil is real. It provides a quick, readily accessible method that can give you a general sense of your oil's quality, especially if you suspect significant adulteration. However, it's important to remember its limitations and to rely on more modern, scientific methods for conclusive authentication. Consider this test a supplementary approach, not a primary means of verification.
5. Label Analysis and Certification Verification: Deciphering the Language of Olive Oil
One of the most effective ways to determine if your olive oil is truly extra virgin is through careful label analysis and certification verification. This method empowers you to assess the authenticity of olive oil before you buy it, leveraging existing regulatory standards and certification programs to make informed decisions. Essentially, you become an olive oil detective, scrutinizing the information provided by the producer to uncover clues about the oil's true nature. This is critical because learning how to tell if olive oil is real starts with understanding what information is reliable.
How it Works: Label analysis involves a multi-pronged approach, examining various aspects of the product label and related documentation to build a picture of the oil’s quality. This includes checking for legally required information, verifying the presence of legitimate quality seals, analyzing dates (production, harvest, and best-by), and assessing the producer’s transparency regarding sourcing and processing methods.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Compliance Check: This method evaluates the label's compliance with legal requirements for olive oil labeling in the region of sale. This ensures the oil meets minimum standards of identity.
- Certification Verification: Look for recognized seals from reputable organizations like the California Olive Oil Council (COOC), North American Olive Oil Association (NAOOA), European Union's Protected Designation of Origin (PDO), or the Italian 100% Qualità Italiana certification. These certifications indicate adherence to stringent quality standards.
- Date Analysis: Examining the harvest date (fresher is always better), best-by date (generally 18-24 months from bottling), and production date gives you valuable insights into the oil's age and potential shelf life.
- Transparency and Traceability: Authentic producers are often transparent about their processes. Look for information about the olive varieties used, the farm or estate of origin, and specific details about production methods.
Pros:
- Non-destructive: You don't need to open the bottle or use any special equipment.
- Proactive: This method allows you to weed out potentially fraudulent products before purchase.
- Comprehensive Assessment: Multiple verification points provide a more holistic assessment of authenticity.
- Leverages Existing Standards: This method relies on existing regulatory frameworks and certification programs, simplifying the process for consumers.
Cons:
- Counterfeiting: Labels and certifications can be forged, requiring careful scrutiny.
- Inconsistent Enforcement: Regulations and their enforcement vary across different countries and regions.
- Requires Knowledge: Understanding different certification systems and standards is necessary to effectively utilize this method.
- Limited Scope: Label analysis cannot detect fraud if the documentation itself is falsified.
Actionable Tips for Savvy Consumers:
- Harvest Date is Key: Prioritize oils with a clear harvest date. Fresher olive oil generally has a more vibrant flavor and higher nutritional value.
- Specificity Matters: Look for oils that specify a particular region or estate rather than just a vague country of origin.
- Recognize the Seals: Familiarize yourself with legitimate certification seals like PDO, PGI, COOC, and NAOOA.
- Variety is the Spice of Life (and Olive Oil): True extra virgin olive oil will often list the specific olive varieties used.
- Dark Glass is Your Friend: Quality producers often use dark glass bottles to protect the oil from light damage.
- Beware of "Pure" and "Light": These terms often indicate refined oils that have undergone significant processing, stripping away much of the flavor and health benefits.
Why This Method Matters: This method deserves a place on this list because it empowers consumers to make educated choices. Investigations by authors like Tom Mueller (author of Extra Virginity) and research from institutions like the UC Davis Olive Center have highlighted the prevalence of olive oil fraud. By understanding how to analyze labels and verify certifications, you can significantly reduce your risk of purchasing adulterated or mislabeled oil. While not foolproof, label analysis, combined with other methods, is a valuable tool in your quest for authentic extra virgin olive oil.
6. Frying Test: Sizzle Your Way to Authentic Olive Oil
This frying test offers a practical, kitchen-based approach to help you tell if olive oil is real. It leverages the heat stability characteristics of real extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) to distinguish it from potential imposters. By observing how the oil behaves when heated, you can gain valuable insights into its authenticity.
This method works by exploiting the fact that pure EVOO has a specific chemical composition that allows it to withstand higher temperatures without significant degradation. Adulterated olive oils, often mixed with lower-quality oils or containing added moisture, react differently to heat. They may exhibit excessive foaming, smoke at lower temperatures, or change color dramatically.
How to Conduct the Frying Test:
- Pour a small amount: Use approximately 2-3 tablespoons of the olive oil in question.
- Choose the right pan: A clean, light-colored pan is ideal, as it allows for better observation of color and clarity changes.
- Heat gradually: Place the pan on the stovetop and heat the oil slowly over medium heat.
- Observe closely: Pay attention to any changes in the oil’s appearance. Look for:
- Foaming: Authentic EVOO produces minimal, quickly dissipating foam. Excessive or persistent bubbles can indicate the presence of moisture or other impurities.
- Color changes: Real olive oil maintains its color relatively well when heated. Noticeable darkening or unusual color shifts might suggest adulteration.
- Smoke point: Genuine EVOO has a relatively high smoke point (generally above 375°F/190°C). If the oil begins to smoke heavily at a lower temperature, it could be a sign of lower quality or adulteration.
Why Use This Test?
This method deserves a place on this list due to its practicality and accessibility. It utilizes readily available kitchen equipment and provides multiple indicators simultaneously, making it a valuable tool for anyone wanting to assess their olive oil's authenticity. It’s a simple way to get a preliminary assessment before committing to using the oil in a larger dish.
Examples of Implementation:
- Chefs often use a quick frying test to gauge the quality of olive oil before incorporating it into their recipes.
- Culinary schools utilize this method to demonstrate the different characteristics of various oils to their students.
- Home cooks, especially in Mediterranean regions, have traditionally relied on similar heating methods to judge the purity of their olive oil.
Pros:
- Uses common kitchen equipment
- Practical and relevant to cooking
- Easy-to-observe results
- Provides multiple indicators
Cons:
- Destructive test (consumes some oil)
- Results can be affected by pan type and heating method
- Some adulterants are designed to mimic EVOO's cooking properties, making this test less definitive than laboratory analysis
- Smoke point can vary among authentic oils due to quality and freshness
Tips for Success:
- Compare your results to a known authentic sample of EVOO if possible.
- Remember that even authentic olive oil's smoke point can vary; however, excessive smoking at normal cooking temperatures should raise a red flag.
While the frying test isn't foolproof, it offers a quick and easy way to gain some insight into your olive oil’s purity. By carefully observing how the oil behaves when heated, you can become a more informed consumer and increase your chances of enjoying the true flavor and health benefits of genuine olive oil. If you’re concerned about how to tell if olive oil is real, this method is a valuable addition to your toolkit.
7. Professional Laboratory Testing: The Definitive Answer to "How to Tell if Olive Oil is Real"
When it comes to definitively answering the question, "how to tell if olive oil is real," professional laboratory testing stands alone. While sensory evaluation and at-home tests can offer clues, only scientific analysis provides irrefutable proof of authenticity and quality. This method involves submitting olive oil samples to specialized laboratories equipped to conduct a battery of chemical tests. These tests delve deep into the oil's composition, revealing its true nature and exposing any potential adulteration.
This approach employs advanced scientific instrumentation and standardized protocols to analyze the oil’s chemical makeup. Techniques like gas chromatography and mass spectrometry are used to identify and quantify the various fatty acids present in the oil, creating a detailed “fingerprint” of its composition. This fingerprint can then be compared against established standards for extra virgin olive oil. Furthermore, these tests can detect the presence of chemical markers indicative of adulteration, such as refined oils or other cheaper vegetable oils. Some labs even utilize DNA testing to verify the olive genetic material, ensuring the oil is derived from the declared olive varieties. This method provides scientifically valid, quantifiable results recognized by regulatory bodies worldwide.
Several successful implementations highlight the power of laboratory testing. The UC Davis Olive Center's landmark 2010 study, which revealed that 69% of imported olive oils failed to meet legal standards for extra virgin olive oil, relied heavily on laboratory analysis. Similarly, the Australian Oils Research Laboratory’s ongoing monitoring program and investigations by the Italian anti-fraud police (NAS) utilize certified labs to ensure olive oil authenticity. These examples underscore the importance of scientific testing in protecting consumers and maintaining market integrity.
Pros and Cons of Professional Laboratory Testing:
Pros:
- Highest accuracy and reliability: Provides definitive answers regarding authenticity and quality.
- Legally admissible evidence: Results can be used in fraud cases.
- Detects sophisticated adulterations: Identifies even subtle blending with lower-quality oils.
- Comprehensive analysis: Offers detailed information on quality parameters beyond just authenticity.
- Objective and quantifiable results: Eliminates subjective biases associated with sensory evaluations.
Cons:
- Expensive: Typically costs $200-$1000 per sample.
- Not readily accessible: Requires sending samples to specialized facilities.
- Requires expert interpretation: Results may be complex and require specialized knowledge to understand.
- Time-consuming: Analysis can take days or weeks.
- Strict protocols: Sample collection and handling procedures must be adhered to for accurate results.
Tips for Utilizing Professional Laboratory Testing:
- Accredited Labs: Choose laboratories accredited by recognized authorities like the International Olive Council (IOC), the American Oil Chemists' Society (AOCS), or the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
- Panel Testing: For valuable collections or suspected fraud, consider combining chemical analysis with sensory evaluation by a trained panel.
- Quality Assurance: Producers can use regular laboratory testing as a crucial part of their quality assurance program.
- Certificates of Analysis: Retailers can request certificates of analysis from their suppliers to verify authenticity.
- University Resources: Some universities offer testing services at more reasonable fees.
Professional laboratory testing deserves its place on this list because it offers the most conclusive way to determine if olive oil is genuine. While other methods provide useful indicators, they lack the scientific rigor and definitive nature of laboratory analysis. For consumers concerned about authenticity or producers aiming for the highest quality standards, professional testing offers peace of mind and invaluable data. This method is particularly useful when dealing with high-value oils, suspected fraud, or legal disputes where irrefutable proof is required. While the cost might be prohibitive for casual consumers checking their everyday olive oil, understanding the power and availability of this method provides crucial context for interpreting the broader discussion around olive oil authenticity.
7 Methods to Verify Olive Oil Authenticity
| Method / Technique | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements 💡 | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold Test (Refrigeration Method) | Low 🔄 (simple steps, minimal skill needed) | Low 💡 (refrigerator only, no special tools) | Moderate 📊 (partial solidification observable) | Home testing, preliminary authenticity check | Accessible, non-destructive, low cost ⭐ |
| Sensory Evaluation (Taste and Smell Test) | Medium 🔄 (requires training and experience) | Very Low 💡 (no equipment, uses senses only) | High 📊 (detects positive/negative sensory traits) | Professional tasting, certification panels, expert use | Immediate results, IOC recognized ⭐ |
| UV Light/Fluorescence Testing | Low-Medium 🔄 (requires UV light, controlled conditions) | Medium 💡 (UV blacklight, dark room) | Moderate 📊 (color fluorescence under UV) | Home or producer preliminary checks | Quick, visual, non-destructive ⭐ |
| Oil Lamp Test | Low 🔄 (easy setup but open flame risk) | Low 💡 (simple lamp or wick setup) | Low 📊 (qualitative flame and smoke evaluation) | Historical/traditional validation, demonstrations | Simple, immediate visual feedback |
| Label Analysis and Certification Verification | Low 🔄 (knowledge-based, no physical tests) | Very Low 💡 (labels and certification review) | Moderate 📊 (assesses documentation, traceability) | Pre-purchase screening, fraud prevention | Non-destructive, regulatory leverage ⭐ |
| Frying Test | Low 🔄 (simple kitchen test) | Very Low 💡 (kitchen pan and stove) | Moderate 📊 (observes foaming, smoke, color changes) | Kitchen use, cooking-related quality indication | Practical, relevant for culinary use |
| Professional Laboratory Testing | High 🔄 (complex procedures, expert analysis) | High 💡 (specialized lab equipment, trained staff) | Very High 📊 (precise chemical and genetic data) | Legal fraud cases, scientific certification, detailed QA | Most accurate, legally recognized ⭐ |
Unlocking the Secrets of Authentic Olive Oil
Knowing how to tell if olive oil is real empowers you to make informed choices that benefit both your palate and your health. From the simple cold test and sensory evaluation to more advanced techniques like UV light testing and label analysis, each method discussed provides another piece of the puzzle. Remember, the most crucial takeaways are to engage your senses, scrutinize labels for certifications, and don't hesitate to conduct at-home tests like the refrigeration or frying test. These simple steps can make all the difference in ensuring you’re experiencing true extra virgin olive oil.
For those interested in diving deeper into the world of olive oil and its authenticity, exploring additional resources can be invaluable. Understanding the origin and production methods can significantly improve your ability to identify real olive oil. Also, consider using website analytics tools to track the performance and engagement of your own online resources if you’re sharing your olive oil knowledge with others. By understanding where your audience is coming from and what content they find most valuable, you can better tailor your information to their needs.
Mastering these techniques isn’t just about avoiding adulterated products; it’s about appreciating the rich culinary heritage and health-boosting properties of real olive oil. It’s about savoring the authentic flavor, aroma, and experience that only genuine olive oil provides. Elevate your culinary journey and unlock a deeper appreciation for this liquid gold – you deserve the real deal! Ready to become an olive oil expert? Continue your olive oil education with Learn Olive Oil and discover even more in-depth knowledge on identifying and appreciating authentic extra virgin olive oil.

Leave a comment