Discovering the Nutritional Powerhouse of Olive Oil
Want to understand the health benefits of olive oil? This listicle breaks down nine essential olive oil nutrition facts, highlighting why this kitchen staple is so good for you. Discover how its composition, from monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) and antioxidants to vitamins E and K, contributes to its anti-inflammatory properties and impacts heart health, blood sugar, and more. We'll also explore the nutritional variations between different olive oil grades. Learn how incorporating the right olive oil can improve your well-being.
1. Rich in Monounsaturated Fatty Acids (MUFAs)
When discussing olive oil nutrition facts, the high concentration of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) is a cornerstone of its health benefits. Olive oil is predominantly composed of these healthy fats, with oleic acid, an omega-9 fatty acid, making up a significant 55-83% of its composition. This is a key reason why olive oil is a staple in heart-healthy diets like the Mediterranean diet. Unlike saturated fats, which can elevate harmful LDL cholesterol levels, MUFAs contribute to maintaining healthy HDL cholesterol (often referred to as "good" cholesterol) while simultaneously reducing LDL ("bad") cholesterol. This balancing act is crucial in promoting cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of heart disease.

One tablespoon (13.5g) of olive oil provides approximately 10g of MUFAs, making it an easy and delicious way to incorporate these beneficial fats into your daily diet. Olive oil is typically liquid at room temperature but may solidify when refrigerated; this change in state does not affect its nutritional value. The high MUFA content contributes significantly to olive oil’s position as a healthy dietary fat. Research, such as The Seven Countries Study by Ancel Keys, first brought the heart-protective benefits of the Mediterranean diet, rich in olive oil, to light, popularizing its use among health-conscious individuals.
Features:
- Contains 73-75% oleic acid (an omega-9 fatty acid)
- One tablespoon (13.5g) contains approximately 10g of MUFAs
- Liquid at room temperature but may solidify when refrigerated
Pros:
- Reduces risk of heart disease
- Helps lower LDL (bad) cholesterol while maintaining HDL (good) cholesterol
- More resistant to oxidation than polyunsaturated fats
- Associated with reduced inflammation
Cons:
- High caloric density (119 calories per tablespoon)
- Can degrade when heated to very high temperatures repeatedly (especially important for reusing oil for frying)
Tips for maximizing the benefits of olive oil's MUFAs:
- Use extra virgin olive oil for cold applications: This preserves the delicate MUFA content and other beneficial compounds, making it ideal for salad dressings, dips, and drizzling over finished dishes.
- Store in a cool, dark place: Protect your olive oil from light and heat to prevent oxidation of the fatty acids, which can degrade its quality and flavor.
- Consume 2-3 tablespoons daily for optimal heart benefits: Incorporate olive oil into your daily meals to reap the rewards of its high MUFA content. Consider using it in place of other less healthy fats.
This high MUFA content firmly establishes olive oil's place on any list concerning olive oil nutrition facts. Its impact on cholesterol management and heart health makes it a valuable addition to a balanced and healthy diet.
2. Potent Source of Antioxidants
When discussing olive oil nutrition facts, its antioxidant power is a standout feature. Olive oil, particularly extra virgin olive oil, is a rich source of antioxidants, which are crucial for protecting your body against cellular damage caused by free radicals. These unstable molecules contribute to oxidative stress, a process linked to aging and various chronic diseases. Olive oil's antioxidant arsenal includes vitamin E, numerous polyphenols (over 30 different types!), and a unique compound called oleocanthal. These compounds work synergistically to neutralize free radicals, effectively reducing inflammation and protecting your cells. The concentration of these beneficial compounds is directly related to the quality of the olive oil, with extra virgin olive oil boasting significantly higher levels than refined varieties.

One remarkable antioxidant in extra virgin olive oil is oleocanthal. This compound exhibits anti-inflammatory properties similar to ibuprofen, a common over-the-counter pain reliever. This contributes to olive oil's overall ability to combat inflammation throughout the body. The combined action of vitamin E, polyphenols, and oleocanthal makes olive oil a valuable dietary component for protecting against cellular damage and promoting overall health.
Features of Olive Oil's Antioxidant Power:
- Contains over 30 different phenolic compounds.
- Extra virgin olive oil has significantly higher antioxidant content than refined varieties.
- Oleocanthal has similar anti-inflammatory effects to ibuprofen.
Pros:
- Protects cells from oxidative damage.
- Contributes to anti-aging benefits for skin and tissues.
- May help reduce the risk of chronic diseases like certain cancers and cognitive decline.
- Provides anti-inflammatory effects.
Cons:
- Antioxidant content degrades over time and with exposure to heat, light, and air.
- Varies significantly between brands and production methods.
Examples of Olive Oil's Antioxidant Benefits:
Studies have shown a correlation between high-quality olive oil consumption and lower rates of certain cancers and cognitive decline, highlighting the potential long-term health benefits of including this antioxidant-rich oil in your diet. Populations in the Mediterranean region, where olive oil is a dietary staple, often exhibit lower incidences of these conditions.
Tips for Maximizing Antioxidant Benefits:
- Look for olive oils with high polyphenol content (this information is sometimes listed on premium bottles).
- Choose oils packaged in dark glass bottles to protect the antioxidants from light damage.
- Use olive oil within 6 months of opening to maximize its antioxidant benefits. Freshness is key!
Popularized By:
The health benefits of high-polyphenol olive oils are often touted by Spanish and Italian olive oil producers. International Olive Council quality standards also play a role in ensuring the quality and antioxidant content of olive oil on the market.
This aspect of olive oil nutrition facts – its potent antioxidant capacity – makes it a valuable addition to a healthy diet. By choosing high-quality extra virgin olive oil and storing it properly, you can harness the full potential of these protective compounds and contribute to your overall well-being.
3. Caloric Density and Fat Content
Olive oil nutrition facts often surprise people when they learn about its caloric density. While lauded for its health benefits, olive oil is a concentrated source of calories, making it crucial to understand its role in a balanced diet. This section delves into the fat content and caloric impact of olive oil, providing practical tips for incorporating it healthfully into your meals.
Olive oil is virtually 100% fat by weight, containing no protein or carbohydrates. A single tablespoon (13.5g) packs approximately 119 calories and 14 grams of total fat. This high caloric density stems from the fact that fat provides 9 calories per gram, compared to 4 calories per gram for both protein and carbohydrates. While this might seem concerning, the type of fat in olive oil is what sets it apart.
Of the 14 grams of total fat per tablespoon, approximately 2 grams are saturated fat, 10 grams are monounsaturated fat (primarily oleic acid), and 2 grams are polyunsaturated fat (including omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids). These monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are considered "healthy fats" and are associated with various health benefits, including improved heart health and reduced inflammation.
Pros of Olive Oil's Fat Content:
- Provides essential fatty acids: Olive oil is a good source of essential fatty acids that the body cannot produce on its own.
- Creates satiety: The fat content contributes to feelings of fullness and satisfaction, potentially reducing overall food intake.
- Healthy fat source for ketogenic and low-carb diets: Its high fat and zero-carb content make it a staple in these dietary approaches.
Cons of Olive Oil's Caloric Density:
- High calorie density can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess: Despite its health benefits, consuming large quantities of olive oil can lead to excess calorie intake and potential weight gain.
- Fat calories add up quickly when used liberally in cooking: It's easy to underestimate the amount of olive oil used when cooking, leading to a higher calorie intake than intended.
Examples of Olive Oil Consumption in a Healthy Diet:
The Mediterranean diet, known for its health benefits, typically includes 3-4 tablespoons of olive oil daily. However, this dietary pattern emphasizes whole foods, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables, allowing individuals to enjoy the benefits of olive oil while maintaining a healthy body weight.
Tips for Managing Olive Oil Intake:
- Measure olive oil rather than pouring freely: Use measuring spoons or a kitchen scale to precisely control your portion sizes and caloric intake.
- Use a spray or mister to distribute smaller amounts evenly when cooking: This technique helps reduce the amount of oil needed while still providing flavor and preventing sticking.
- Replace butter or margarine with olive oil for a better nutritional profile despite similar calories: While the calorie content is similar, olive oil offers a healthier fat profile.
This understanding of olive oil nutrition facts, particularly its caloric density and fat composition, is essential for anyone looking to incorporate its health benefits while managing their overall calorie intake. By being mindful of portion sizes and using smart cooking techniques, you can enjoy the flavor and health benefits of olive oil as part of a balanced diet.
4. Vitamin E and K Content
Olive oil isn't just a source of healthy fats; it also contributes to your daily intake of essential fat-soluble vitamins, specifically vitamin E and vitamin K. This further solidifies its place as a nutritional powerhouse and a key component of healthy diets like the Mediterranean diet. Understanding the vitamin content of olive oil as part of exploring olive oil nutrition facts empowers you to make informed dietary choices.
One tablespoon of olive oil provides approximately 1.9mg of vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol), fulfilling about 13% of the recommended daily value. It also delivers around 8.1μg of vitamin K, contributing approximately 7% of the daily value. These vitamins play vital, albeit distinct, roles in maintaining overall health.
Vitamin E acts as a potent antioxidant, protecting your cells from damage caused by free radicals. These unstable molecules are byproducts of normal metabolism but can contribute to aging and various health problems when they accumulate. Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting, ensuring your body can stop bleeding effectively in case of injury. It also plays a role in bone health and other bodily functions.
Olive oil's inherent resistance to oxidation helps preserve these delicate vitamins, ensuring you receive their full benefits. This natural preservation is a significant advantage, particularly when considering storage and cooking practices.
Features and Benefits:
- Antioxidant Protection (Vitamin E): Shields cells from oxidative stress and damage.
- Blood Clotting and Bone Health (Vitamin K): Supports proper coagulation and contributes to bone maintenance.
- Natural Preservation: Olive oil's resistance to oxidation helps maintain vitamin potency.
Pros:
- Easy Integration: Easily incorporated into your diet through regular culinary use.
- Enhanced Absorption: Helps your body absorb fat-soluble vitamins from other foods consumed in the same meal.
- Stable Nutrient Source: Provides stable forms of vitamin E and K that aren't easily degraded during storage.
Cons:
- Variable Vitamin Content: The precise amount of vitamins can fluctuate based on the olive variety, growing conditions, and processing methods.
- Fat-Dependent Absorption: Requires dietary fat for optimal absorption, although olive oil itself provides this fat.
Tips for Maximizing Benefits:
- Drizzle over Vegetables: Enhance the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins from vitamin-rich vegetables by drizzling them with olive oil.
- Combine with Leafy Greens: Amplify the benefits of vitamin K by combining olive oil with leafy greens, which are naturally rich in this nutrient.
- Choose Extra Virgin Olive Oil: Opt for extra virgin olive oil, as it typically contains the highest levels of vitamins and antioxidants.
Nutritional researchers studying the health benefits of the Mediterranean diet have popularized the use of olive oil for its vitamin content, among other nutritional advantages. This diet, known for its emphasis on whole foods and healthy fats, showcases the beneficial role olive oil can play in promoting overall well-being. By understanding these olive oil nutrition facts, particularly the contributions of vitamins E and K, you can make more informed decisions about incorporating this valuable oil into your daily diet.
5. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Inflammation is a natural bodily response to injury or infection. However, chronic, low-grade inflammation can silently contribute to a range of serious health issues including heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, and certain cancers. When considering olive oil nutrition facts, its potent anti-inflammatory properties deserve significant attention. These properties solidify olive oil's position as a cornerstone of the healthy Mediterranean diet.
Olive oil contains a diverse range of phenolic compounds that contribute to its anti-inflammatory effects. The most notable of these is oleocanthal, a unique compound that has been scientifically proven to work similarly to ibuprofen, a common non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Oleocanthal inhibits the production of COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, which are key players in the inflammatory process. This makes olive oil a valuable dietary tool for managing inflammation naturally. The distinct, peppery "sting" you feel at the back of your throat when tasting high-quality extra virgin olive oil is a direct result of the oleocanthal content. This sensation is a helpful indicator of the oil's potential anti-inflammatory potency.
Extra virgin olive oil typically contains between 5-200 mg/kg of oleocanthal, with variations depending on factors like olive variety, growing conditions, and extraction methods. Beyond oleocanthal, olive oil boasts a multitude of other polyphenols, including oleuropein, hydroxytyrosol, and tyrosol, which work synergistically to reduce inflammatory markers in the body.
Features & Benefits of Olive Oil's Anti-Inflammatory Properties:
- Oleocanthal's ibuprofen-like action: Targets the same inflammatory pathways as NSAIDs, offering natural pain relief and inflammation reduction.
- Multiple polyphenols: Provides a broad spectrum of anti-inflammatory activity.
- Reduces expression of inflammatory genes: Addresses inflammation at a fundamental level.
- Decreases production of inflammatory cytokines: Lowers levels of signaling molecules that promote inflammation.
- Benefits don't diminish with regular consumption: Long-term use continues to provide anti-inflammatory effects.
Pros:
- May help manage symptoms of inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Reduces overall inflammatory burden, contributing to long-term health.
- Safe and well-tolerated as part of a healthy diet.
Cons:
- Anti-inflammatory compounds are diminished in processed or low-quality oils. Opt for extra virgin olive oil.
- High heat from cooking can reduce some anti-inflammatory properties. Consider using olive oil as a finishing oil or for low-heat cooking.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Studies show that consuming 3-4 tablespoons of extra virgin olive oil daily can significantly lower inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). These markers are key indicators of systemic inflammation and are linked to various chronic diseases.
Tips for Maximizing Anti-Inflammatory Benefits:
- Choose high-quality extra virgin olive oil: Look for oils with a robust, peppery flavor at the back of the throat, indicating higher oleocanthal content.
- Use as a finishing oil: Drizzle over salads, soups, and other dishes after cooking to preserve the heat-sensitive anti-inflammatory compounds.
- Incorporate into a balanced diet: Olive oil complements a Mediterranean-style diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Popularized By:
Dr. Gary Beauchamp's groundbreaking research in 2005 identified oleocanthal's ibuprofen-like properties, bringing olive oil's anti-inflammatory power to the forefront. Researchers at the University of Athens have further investigated olive oil's crucial role in the health benefits associated with the Mediterranean diet.
Including olive oil in your diet is a simple yet powerful way to harness the benefits of this ancient superfood. By understanding the olive oil nutrition facts, particularly its anti-inflammatory properties, you can make informed choices to improve your overall health and well-being.
6. Heart Health Benefits
Olive oil's remarkable impact on cardiovascular health earns it a prominent place on any list of olive oil nutrition facts. This "liquid gold" has been a cornerstone of the heart-healthy Mediterranean diet for centuries, and modern science continues to validate its protective effects. Consuming olive oil as part of a balanced diet is strongly associated with improved cardiovascular health and a reduced risk of heart disease. But how exactly does it work?
Olive oil’s heart-healthy magic stems from its unique nutritional profile. It’s rich in monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), particularly oleic acid, which plays a key role in improving cholesterol levels. Specifically, olive oil helps lower LDL ("bad") cholesterol while maintaining or even increasing HDL ("good") cholesterol, thus improving the overall cholesterol ratio. This is crucial because high LDL cholesterol contributes to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke. Furthermore, olive oil contains potent antioxidants, including polyphenols, which help prevent the oxidation of LDL cholesterol. Oxidized LDL is even more harmful as it contributes to inflammation and the formation of arterial plaques.
Beyond cholesterol management, olive oil contributes to heart health through several other mechanisms. It helps reduce both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, further lowering the strain on the cardiovascular system. Olive oil also improves endothelial function, meaning it helps the lining of blood vessels stay healthy and flexible, promoting healthy blood flow. Finally, its anti-inflammatory properties contribute to reducing inflammation in the blood vessels, further mitigating the risk of heart disease.
Features and Benefits of Olive Oil for Heart Health:
- Improves cholesterol ratio: Lowers LDL cholesterol while preserving HDL cholesterol.
- Reduces blood pressure: Lowers both systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings.
- Contains antioxidants: Prevents LDL oxidation, reducing plaque formation.
- Improves endothelial function: Promotes healthy and flexible blood vessels.
Pros:
- Significant risk reduction: Associated with a 30% lower risk of cardiovascular events in long-term studies like the PREDIMED study.
- Long-term benefits: Benefits accumulate with consistent, long-term consumption.
- Multifaceted protection: Works through multiple pathways to protect heart health.
Cons:
- Requires healthy dietary context: Benefits are maximized when olive oil replaces less healthy fats, not when added to an already unhealthy diet.
- Needs consistency: Requires consistent consumption for optimal effects.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- The PREDIMED (PREvención con DIeta MEDiterránea) study, led by Dr. Miguel Martínez-González, demonstrated a remarkable 30% reduction in major cardiovascular events among participants following a Mediterranean diet supplemented with extra-virgin olive oil.
- The Lyon Diet Heart Study showed that adopting a Mediterranean diet rich in olive oil offered significant protection against secondary heart attacks.
Tips for Achieving Cardiovascular Benefits with Olive Oil:
- Aim for at least 2 tablespoons daily: Incorporate this amount into your daily diet for optimal cardiovascular benefits.
- Replace unhealthy fats: Substitute butter, margarine, and other less healthy cooking oils with olive oil.
- Synergistic effects: Combine olive oil with other heart-healthy foods like nuts, fatty fish, and vegetables for even greater benefits.
Popularized By:
- Dr. Miguel Martínez-González and the PREDIMED research team
- American Heart Association's dietary recommendations
In conclusion, incorporating olive oil into a balanced diet is a powerful strategy for promoting heart health. Its beneficial effects on cholesterol, blood pressure, endothelial function, and inflammation make it a valuable ally in the fight against cardiovascular disease. Remember to use it consistently and as a replacement for unhealthy fats to fully reap its rewards. By understanding these olive oil nutrition facts, you can make informed choices to support your long-term cardiovascular well-being.
7. Impact on Blood Sugar and Diabetes
Among the numerous olive oil nutrition facts, its positive influence on blood sugar regulation and diabetes management stands out. Olive oil, unlike many other fats and oils, plays a crucial role in moderating blood glucose levels and improving insulin sensitivity. This means it helps prevent dramatic spikes in blood sugar after meals and can enhance the body's responsiveness to insulin over time. These properties are particularly significant for individuals with, or at risk of developing, type 2 diabetes. It's important to note that these benefits are primarily realized when olive oil replaces less healthy fats in the diet, rather than being added on top of existing fat intake.

This positive impact on blood sugar control stems from several key components of olive oil: its low glycemic impact, the presence of insulin-sensitizing polyphenols, and the glucose-regulating properties of oleic acid. Olive oil is also known to reduce oxidative stress, a contributing factor to insulin resistance. More specifically, the polyphenols in olive oil enhance insulin action, allowing cells to utilize glucose more effectively. Oleic acid, the primary fatty acid in olive oil, contributes to improved glucose metabolism.
Examples of Successful Implementation: Research has consistently demonstrated that incorporating olive oil into carbohydrate-rich meals can lower the overall glycemic response. For example, studies have shown that adding olive oil to a meal of pasta significantly reduces the subsequent blood sugar spike compared to consuming pasta without olive oil.
Actionable Tips for Readers:
- Add olive oil to carbohydrate-containing meals: This helps slow glucose absorption, leading to more stable blood sugar levels.
- Use in salad dressings: This reduces the glycemic impact of the entire meal.
- Combine with vinegar: The combination of olive oil and vinegar has been shown to have synergistic effects on blood sugar management.
When and Why to Use This Approach: Individuals with type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, or those looking to maintain healthy blood sugar levels can benefit from including olive oil as part of a balanced diet. It is particularly helpful for managing post-meal blood sugar spikes.
Pros:
- May reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by up to 16%, according to meta-analyses.
- Helps maintain more stable blood sugar levels.
- Can be used in place of less healthy fats without negatively impacting glycemic control.
Cons:
- Benefits are mostly seen when replacing less healthy fats, not when added to an existing diet.
- Still calorie-dense, requiring portion control for those managing weight along with diabetes.
The impact of olive oil on blood sugar and diabetes deserves a prominent place in any discussion of olive oil nutrition facts. Its demonstrated ability to improve insulin sensitivity, moderate blood sugar levels, and potentially reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes makes it a valuable dietary component for supporting metabolic health. Recommendations from organizations like the American Diabetes Association and research by experts like Dr. Jordi Salas-Salvadó on the Mediterranean diet further underscore the importance of olive oil in diabetes prevention and management.
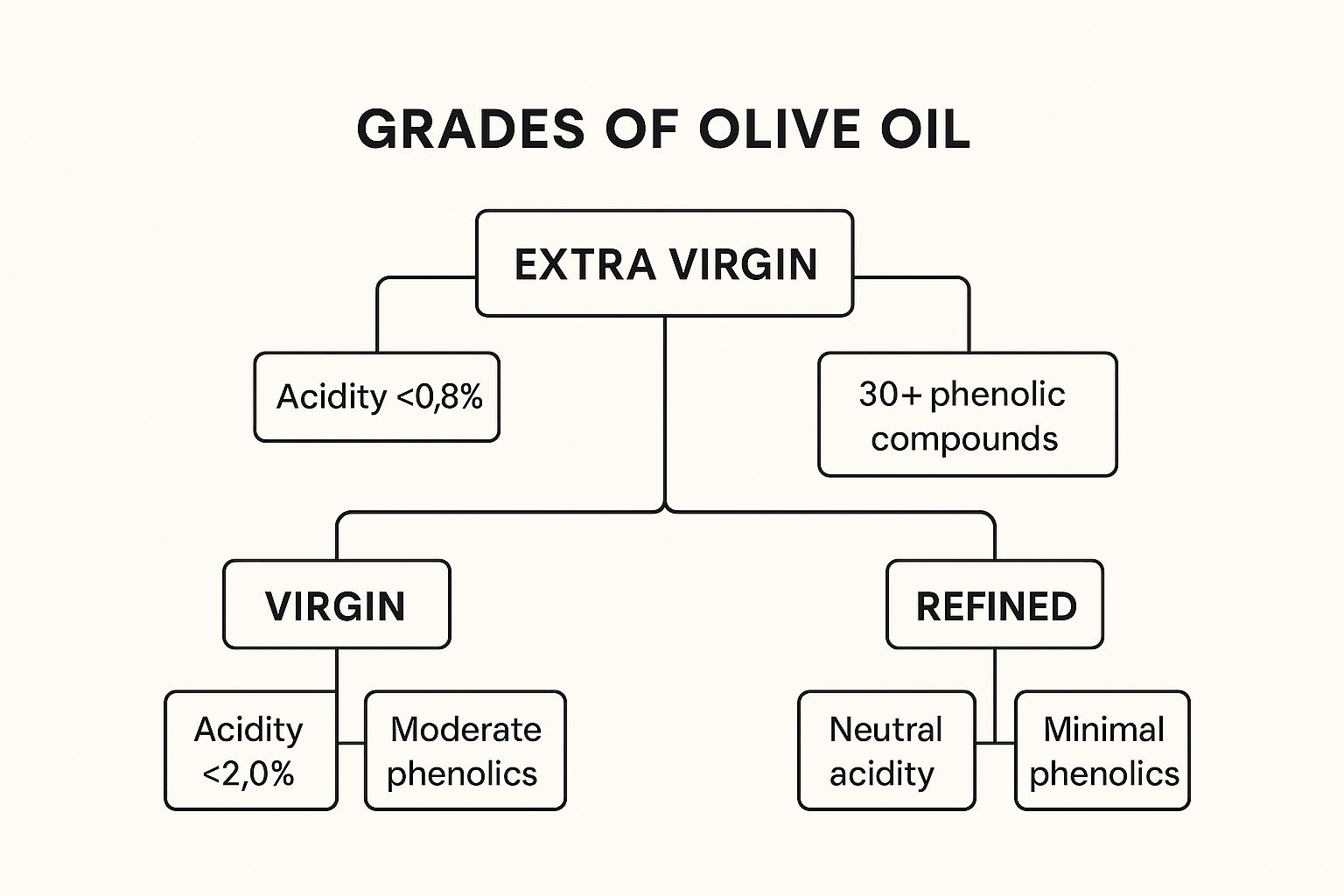
8. Different Grades and Their Nutritional Variations
Understanding the different grades of olive oil is crucial for maximizing the nutritional benefits you receive. While all olive oils are derived from olives, the processing methods and resulting quality classifications significantly impact their nutritional composition. This directly affects the olive oil nutrition facts you should consider when making a purchase.
Olive oil is graded based on factors like acidity levels, extraction methods, and sensory qualities. The primary grades are:
-
Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO): Considered the gold standard, EVOO is produced through a purely mechanical, cold-pressing process without the use of heat or chemicals. This method preserves the maximum amount of natural antioxidants, vitamins, and phenolic compounds. EVOO boasts a low acidity level (below 0.8%) and possesses a distinct, fruity flavor.
-
Virgin Olive Oil: Also produced mechanically, virgin olive oil has a slightly higher acidity level (up to 2.0%) compared to EVOO. It still offers a good source of nutrients but may have a milder flavor profile.
-
Refined Olive Oil/Light Olive Oil: These oils undergo refining processes, including chemical treatments and heat, to neutralize strong flavors and odors. This process, while increasing the smoke point, significantly diminishes the nutritional value, stripping away many of the beneficial antioxidants and phenolic compounds found in EVOO and virgin olive oil.
Nutritional Variations and Olive Oil Nutrition Facts:
The different production methods drastically impact the olive oil nutrition facts. For example, EVOO contains over 30 phenolic compounds, which contribute to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Refined oils, on the other hand, contain few, if any, of these valuable compounds. The color and sensory attributes of the oil (aroma, taste) also reflect these differing nutrient profiles. Unfiltered EVOO often contains more beneficial plant compounds due to the presence of fine olive particles.
Pros of Higher Grades:
- Maximum Antioxidant and Vitamin Retention: EVOO retains the highest levels of naturally occurring antioxidants and vitamins, offering substantial health benefits.
- Enhanced Anti-inflammatory Properties: Higher-grade oils provide a greater concentration of anti-inflammatory compounds, potentially reducing chronic inflammation.
- Rich in Beneficial Plant Compounds: Unfiltered oils, particularly EVOO, contain more beneficial plant particles and compounds.
Cons of Higher Grades:
- Lower Smoke Points: EVOO and virgin olive oil have lower smoke points, making them less suitable for high-heat cooking methods like frying.
- Higher Cost: Premium nutritional grades like EVOO are more expensive due to their production methods and superior quality.
- Shorter Shelf Life: The most nutritious olive oils tend to have a shorter shelf life than refined oils.
Examples and Studies:
Numerous studies demonstrate the superior nutritional benefits of EVOO. For example, research shows that EVOO provides significantly greater reductions in oxidative stress markers compared to refined olive oil, highlighting its protective effects against cellular damage.
Tips for Utilizing Different Grades:
- Maximize Nutritional Benefits: Use EVOO for drizzling over salads, in dressings, dips, and for low-heat cooking methods like sautéing to preserve its valuable nutrients.
- High-Heat Applications: Reserve refined olive oils for high-heat cooking applications like frying and roasting where a higher smoke point is essential.
- Ensure Freshness: Look for the harvest date on premium olive oils to ensure freshness and optimal nutrient preservation.
Popularized By:
International organizations like the International Olive Council (IOC), along with regional bodies such as the California Olive Oil Council and the North American Olive Oil Association, have established grading standards and quality seals to help consumers identify authentic and high-quality olive oils. These standards contribute to consumer awareness regarding olive oil nutrition facts and quality.
By understanding the differences in olive oil grades and their nutritional variations, you can make informed choices that align with your health goals and culinary needs. Choosing the right grade ensures you reap the full spectrum of benefits this healthy fat has to offer.
9. Olive Oil's Impact on Overall Health
Olive oil, a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet, offers a wealth of nutritional benefits that extend far beyond just its delicious flavor. It's packed with healthy fats, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory compounds, contributing to overall well-being and reducing the risk of various health problems. Understanding how these components interact within the body is key to appreciating the true value of including olive oil in your diet.
This infographic visualizes the interconnectedness of olive oil's components and their effects on different aspects of health. The central concept is Olive Oil Consumption, which branches out to its key benefits.
As the infographic demonstrates, the high monounsaturated fat content in olive oil (primarily oleic acid) plays a crucial role in Cardiovascular Health. It helps lower LDL ("bad") cholesterol while potentially raising HDL ("good") cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke. The infographic also highlights the link between olive oil's antioxidant content (polyphenols like hydroxytyrosol and oleocanthal) and Reduced Inflammation. This contributes to protection against chronic diseases like arthritis, cancer, and Alzheimer's. Furthermore, olive oil's impact on Metabolic Health is illustrated, connecting it to improved insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control, which can help prevent type 2 diabetes. Finally, the infographic touches on the potential benefits for Brain Health, suggesting a role in cognitive function and protection against neurodegenerative diseases.
Olive oil's impressive nutritional profile makes it a valuable addition to a healthy diet. The infographic effectively illustrates the interconnected nature of its benefits, demonstrating how regular olive oil consumption can contribute to improved well-being across multiple body systems.
To reap the maximum health benefits from olive oil, opt for extra virgin olive oil (EVOO), as it retains more of the beneficial antioxidants and polyphenols. Incorporate it into your daily diet by using it as a salad dressing, for dipping bread, or in cooking at lower temperatures. Remember, while olive oil is undeniably healthy, moderation is key. Like any fat, it is calorie-dense, so be mindful of portion sizes.
Pros of including olive oil in your diet:
- Improves cardiovascular health
- Reduces inflammation
- Supports metabolic health
- May benefit brain health
- Enhances the flavor of food
Cons of excessive olive oil consumption:
- High in calories
- Can cause digestive upset if consumed in large quantities
- May interact with certain medications (consult your doctor)
By understanding the olive oil nutrition facts and its various benefits, as visualized in the infographic, you can make informed choices about incorporating this healthy fat into your diet and improving your overall well-being. This reinforces why understanding olive oil's impact on health deserves a place on this list.
Olive Oil Nutrition Facts: 9 Key Aspects Compared
| Aspect | Rich in Monounsaturated Fatty Acids (MUFAs) ⭐📊 | Potent Source of Antioxidants ⭐📊 | Caloric Density and Fat Content ⚡📊 | Vitamin E and K Content ⭐💡 | Anti-Inflammatory Properties ⭐📊 | Heart Health Benefits ⭐📊 | Impact on Blood Sugar and Diabetes ⭐📊 | Different Grades and Their Nutritional Variations ⭐🔄💡 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Low – simple daily use or cooking | Medium – requires selecting high-quality EVOO | Low – easy to measure and incorporate | Low – use as dressing or cooking | Medium – best as finishing oil | Low – daily inclusion in diet | Low – add to meals | Medium – choose grades based on use and quality |
| Resource Requirements ⚡ | Minimal – regular access to olive oil | High – need premium extra virgin oils | Minimal – control portions | Minimal – regular olive oil use | Medium – high-oleocanthal EVOO preferred | Minimal – incorporate staple oil | Minimal – dietary changes | Medium – purchase cost varies by grade |
| Expected Outcomes 📊 | Improved cholesterol, heart health | Reduced oxidative stress, anti-aging | Satiety and energy intake control | Antioxidant protection, blood clotting | Reduced inflammation, symptom management | Lower cardiovascular risks | Better blood glucose control | Varied nutrient and antioxidant retention |
| Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Daily cooking, salads, and dressings | Cold dishes, raw use to preserve antioxidants | Weight management, ketogenic diet | Enhancing vitamin absorption in meals | Managing chronic inflammation | Cardiovascular disease prevention | Diabetes and blood sugar management | Choosing oil for cooking vs. finishing and health benefits |
| Key Advantages ⭐ | Heart-healthy fatty acids, anti-inflammatory | Powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties | Easy to control calories with measured use | Provides essential fat-soluble vitamins | NSAID-like natural anti-inflammatory effect | Proven multi-path cardiovascular protection | Supports insulin sensitivity and glycemic control | Nutritional quality varies by processing and grade |
| Limitations | Degrades if overheated repeatedly | Antioxidants degrade over time and heat | High calorie density may cause weight gain | Vitamin levels vary by source and processing | Loss of compounds with heat and processing | Requires replacement of unhealthy fats | Requires portion control due to calories | Higher cost and shorter shelf life for high-grade oils |
Embrace the Nutritional Gold: Making Olive Oil a Part of Your Healthy Lifestyle
From its rich monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) profile and potent antioxidant content to its beneficial impact on heart health and blood sugar levels, understanding olive oil nutrition facts empowers you to make informed dietary choices. We've explored the impressive array of vitamins, like vitamin E and K, present in olive oil, delved into its anti-inflammatory properties, and even touched on the varying nutritional profiles of different olive oil grades. Remember, extra virgin olive oil generally boasts the highest concentration of beneficial compounds. One of the key takeaways is the importance of incorporating this nutritional powerhouse into your daily meals. When preparing meals ahead of time or packing leftovers that include olive oil, consider using high-quality takeout containers to maintain its freshness and prevent spills. According to When Shopping For Takeut Containers, These Are the Most Important Factors from MrTakeOutBags.com, choosing the right container is crucial for preserving food quality.
Mastering these olive oil nutrition facts is invaluable for anyone striving to improve their overall well-being. By consciously choosing high-quality olive oil and incorporating it into your diet, you're not just adding flavor, but also investing in long-term health benefits. From reducing your risk of chronic diseases to simply enjoying more vibrant meals, the advantages are numerous.
Ready to dive even deeper into the world of olive oil? Discover the nuances of olive oil grades, learn expert selection and tasting techniques, and explore delicious culinary applications with Learn Olive Oil . This comprehensive resource will equip you with everything you need to know to fully appreciate and benefit from the remarkable nutritional power of olive oil.

Leave a comment