Decoding Olive Oil: A Guide to Culinary Excellence
This guide clarifies the different types of olive oil for cooking, empowering you to choose the best one for every dish. Learn about seven distinct varieties, from extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) to flavored oils, and understand how their unique flavors and properties impact your cooking. Whether sautéing vegetables, dressing a salad, or dipping bread, selecting the right olive oil elevates taste and maximizes health benefits. This listicle provides the essential knowledge for informed olive oil choices.
1. Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO)
Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) sits at the pinnacle of the olive oil hierarchy, representing the highest quality and purest form available. When exploring types of olive oil for cooking, understanding EVOO's unique characteristics is essential. It’s derived solely through mechanical means, a process that avoids the use of heat or chemicals, preserving the natural integrity of the olives. This meticulous extraction method ensures that EVOO retains the maximum amount of flavor, aroma, and nutritional benefits compared to other olive oil varieties. The process, often referred to as "cold-pressing," must occur within 24 hours of harvesting to maintain the oil's exceptional quality and low acidity, legally mandated to be below 0.8%. This contributes to its vibrant flavor profile and superior health benefits.
EVOO’s distinct characteristics are what set it apart. Its low acidity level, a testament to its purity, is a key feature. The cold-pressed extraction method, another defining characteristic, ensures the preservation of delicate flavors and beneficial compounds like antioxidants and polyphenols. These contribute to the oil's distinctive fruity, peppery, or grassy flavors, which can vary based on the olive cultivar and terroir. However, this quality also impacts its relatively low smoke point, typically between 375-405°F (190-207°C).
The numerous pros of using EVOO are compelling. It boasts the highest nutritional value among olive oil types, packed with healthy monounsaturated fats and natural antioxidants, promoting heart health and overall well-being. Its rich and complex flavor profile elevates dishes, making it ideal for drizzling over finished creations and adding a touch of culinary finesse. Think of vibrant salads, grilled vegetables, or a simple bowl of pasta elevated by a generous drizzle of EVOO. It also serves as a flavorful base for pasta sauces and marinades, lending depth and complexity.
However, EVOO does have some drawbacks. It's typically the most expensive option among olive oil types, reflecting its superior quality and production process. Its lower smoke point makes it unsuitable for high-heat cooking methods like deep frying or searing, as these can degrade the oil and compromise its flavor. Furthermore, its robust flavor can be overpowering in some dishes, and it has a shorter shelf life compared to refined oils.
Examples of EVOO's successful implementation abound, particularly in Mediterranean cuisine. It forms the backbone of countless salad dressings, adding a vibrant, fruity dimension. Drizzled over grilled vegetables, it enhances their natural sweetness and adds a touch of elegance. It's also frequently used as a finishing oil for soups and stews, providing a final flourish of flavor and aroma.
To maximize the lifespan and quality of your EVOO, proper storage is crucial. Store it in a dark, cool place away from heat and light. Aim to use it within 18-24 months of the harvest date for optimal flavor. Before using, taste a small amount to understand its specific flavor profile, as this can vary significantly between brands and harvests. Remember, avoid using EVOO for deep frying or high-heat searing due to its low smoke point. Popular brands known for their high-quality EVOO include California Olive Ranch, Colavita, Lucini Italia, and Cobram Estate.
The following infographic helps guide you on when to use EVOO based on your cooking temperature and desired flavor outcome.
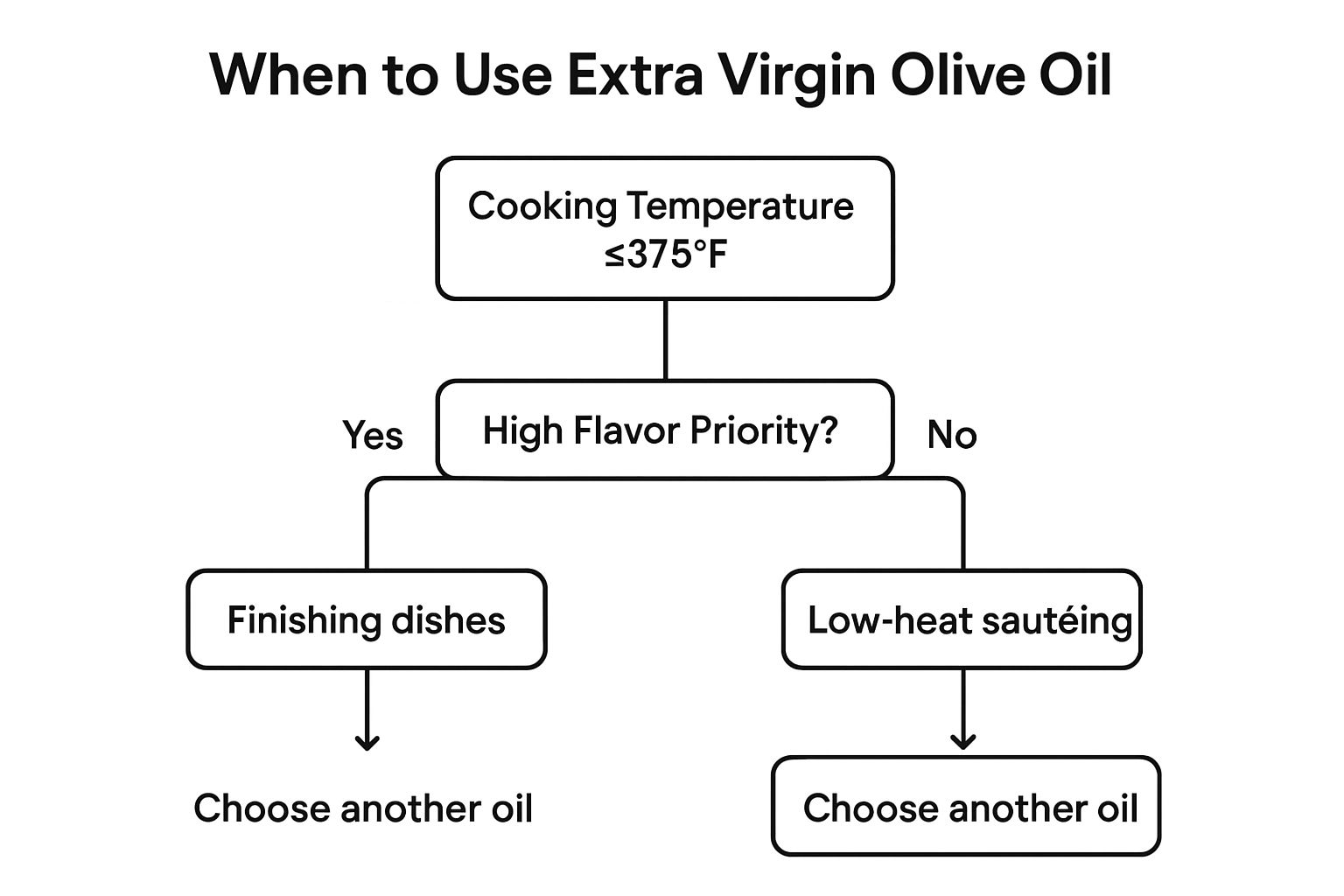
This simple decision tree clarifies the ideal applications of EVOO. If your cooking temperature is below 375°F and you prioritize high flavor, EVOO is excellent as a finishing oil. If flavor is less critical, it can be used for low-heat sautéing. However, if your cooking temperature exceeds 375°F, another oil is recommended. Ultimately, choosing the right type of olive oil depends on understanding the nuances of each variety and aligning them with your culinary needs. With its unique characteristics and health benefits, EVOO holds a deserved place as a staple in kitchens worldwide.
2. Virgin Olive Oil: A Versatile All-Rounder for Everyday Cooking
When exploring the different types of olive oil for cooking, virgin olive oil emerges as a strong contender, offering an excellent balance between quality, flavor, and affordability. Sitting just below extra virgin olive oil in the hierarchy of olive oil grades, virgin olive oil provides a versatile option for a wide range of culinary applications. It's mechanically extracted, just like extra virgin, ensuring a chemical-free process that preserves the natural goodness of the olives. While it might not boast the same intense fruity notes as its extra virgin counterpart, virgin olive oil still delivers a pleasant flavor profile suitable for many dishes. This makes it a popular choice for home cooks seeking a reliable and cost-effective option for their everyday cooking needs.
Understanding Virgin Olive Oil Production and Characteristics
Virgin olive oil, like all olive oils, begins its journey with the harvesting of olives. These olives are then crushed and processed through mechanical means, including pressing or centrifugation, to extract the oil. Crucially, no heat or chemicals are used during this extraction process, preserving the natural characteristics and flavors of the olives. The distinguishing factor between extra virgin and virgin olive oil lies in the acidity level. Virgin olive oil has a slightly higher acidity level, ranging between 0.8% and 2.0%, compared to extra virgin's maximum of 0.8%. This difference in acidity contributes to subtle variations in flavor and aroma. While extra virgin olive oil is known for its robust and peppery notes, virgin olive oil tends to have a milder, more delicate flavor. It retains a good level of fruitiness, making it a palatable and enjoyable option for everyday cooking. With a smoke point around 420°F (215°C), virgin olive oil is suitable for medium-heat cooking methods like sautéing, baking, and roasting.
The Advantages of Choosing Virgin Olive Oil
Virgin olive oil presents several advantages that make it a popular choice among consumers. First and foremost, it offers a better value proposition than extra virgin olive oil. While still retaining a good flavor profile and most of the nutritional benefits, virgin olive oil comes at a more accessible price point. This makes it an attractive option for those looking to incorporate high-quality olive oil into their daily cooking without breaking the bank. Its versatility is another key advantage. Virgin olive oil is well-suited to a variety of cooking methods, from sautéing vegetables to roasting meats and creating homemade salad dressings. Its relatively high smoke point allows for comfortable medium-heat cooking without the risk of the oil degrading and producing harmful compounds. Furthermore, virgin olive oil retains a significant portion of the nutritional benefits found in olives, including monounsaturated fats, antioxidants, and vitamins.
Weighing the Pros and Cons
While virgin olive oil offers numerous benefits, it's important to acknowledge its limitations compared to extra virgin olive oil. The primary difference lies in the flavor complexity. Virgin olive oil lacks the intense fruity and peppery notes that characterize extra virgin olive oil, resulting in a more subdued flavor profile. It also has a slightly lower antioxidant content. Consequently, virgin olive oil is generally not recommended for finishing dishes where the nuanced flavor of extra virgin would shine. Additionally, the quality of virgin olive oil can vary between brands, making it essential to choose reputable producers.
Practical Applications and Tips for Using Virgin Olive Oil
Virgin olive oil shines in various cooking scenarios. It's an excellent choice for sautéing vegetables, providing a healthy and flavorful base. It can be used as the foundation for homemade salad dressings, lending a subtle olive flavor without overpowering other ingredients. Pasta dishes also benefit from the addition of virgin olive oil, adding richness and a touch of Mediterranean flair. When roasting meats at medium temperatures, virgin olive oil offers a good balance of flavor and heat stability.
To maximize the quality and freshness of your virgin olive oil, look for harvest dates on the bottle and choose more recent harvests. Store the oil in a cool, dark place away from direct sunlight and heat to preserve its flavor and nutritional value. Remember, virgin olive oil represents a smart compromise between quality and price, making it a valuable addition to any kitchen. It's a versatile and reliable cooking oil that can elevate everyday meals without compromising on flavor or nutritional value. Popular brands like Bertolli, Pompeian, Star Olive Oil, and Filippo Berio all offer readily available options for consumers.
3. Pure Olive Oil (Refined Olive Oil)
When exploring the world of olive oils for cooking, "pure" olive oil often causes confusion. Unlike "extra virgin" or "virgin," the term "pure" doesn't indicate a higher quality. Instead, "pure olive oil" signifies a blend of refined olive oil and virgin olive oil, typically containing about 85% refined oil. This unique composition gives it a distinct place in the kitchen, offering specific advantages for certain cooking styles. It represents a practical and economical choice for everyday cooking, particularly when the robust flavor of virgin olive oils isn't desired.

Refined olive oil is made from olive oil that doesn't meet the standards for virgin grades. This lower-quality oil undergoes a refining process, which includes deodorization and filtration, to remove impurities, strong flavors, and any defects. This process results in a neutral-tasting, colorless oil. While refining strips away some of the natural antioxidants and polyphenols present in virgin olive oils, blending it with virgin olive oil adds back some of the flavor and health benefits, creating a balanced product. This blending process also helps to improve the overall quality and flavor of the refined olive oil.
One of the key features of pure olive oil is its higher smoke point—around 465°F (240°C). This makes it a versatile option for various cooking methods, including high-heat sautéing, stir-frying, and even some shallow frying. Unlike delicate extra virgin olive oil, which has a lower smoke point and can break down and release harmful compounds at high temperatures, pure olive oil remains stable and safe for these cooking applications. This characteristic is essential for those who regularly cook with high heat or prefer cooking methods like stir-frying, where a neutral-flavored oil is preferred.
Pure olive oil's neutral flavor profile also makes it a valuable asset in the kitchen. While some appreciate the peppery and fruity notes of extra virgin olive oil, it can be overpowering in certain dishes. Pure olive oil allows the natural flavors of ingredients to shine through without imparting any distinct olive taste. This makes it ideal for baking, where a neutral flavor is crucial, and for preparing delicate sauces or marinades where the focus is on other flavor components.
Furthermore, pure olive oil typically has a longer shelf life than virgin olive oils due to the refining process. Its consistent quality makes it a reliable choice for large-scale commercial food preparation and home cooks alike. This stability ensures that the oil performs consistently across different batches and remains usable for an extended period, reducing waste and providing value for money.
While pure olive oil offers numerous benefits, it's essential to acknowledge its drawbacks. The refining process, while creating a more stable and versatile oil, diminishes some of the nutritional value present in virgin olive oils. It contains fewer antioxidants and polyphenols, which are beneficial compounds linked to various health benefits. Therefore, if maximizing health benefits is a primary concern, extra virgin olive oil remains the superior choice for low-heat cooking and dressings.
Pros:
- Versatile for all cooking methods
- Higher smoke point allows high-heat cooking
- Neutral taste won't overpower dishes
- More affordable than virgin grades
- Stable for long-term storage
Cons:
- Lower nutritional value than virgin oils
- Minimal olive flavor
- Heavily processed
- Fewer antioxidants and polyphenols
Examples of Use:
- High-heat stir-frying and sautéing
- Deep frying applications (in moderation)
- Baking where neutral flavor is desired
- Commercial food preparation
Tips for Using Pure Olive Oil:
- Choose pure olive oil for high-heat cooking methods like stir-frying and pan-searing.
- Use pure olive oil when a neutral oil is required, allowing the flavors of your ingredients to take center stage.
- It’s a good option for beginners learning to cook with olive oil, offering versatility and a higher margin of error in terms of heat.
- While suitable for deep frying, use it in moderation due to its slightly lower smoke point compared to other high-heat oils like refined avocado oil.
Popular Brands of Pure Olive Oil:
- Bertolli Classic
- Pompeian Classic
- Star Pure Olive Oil
- Carapelli
Pure olive oil occupies a distinct niche within the spectrum of olive oil types for cooking. By understanding its unique characteristics, both advantages and limitations, cooks can make informed decisions about when and how to incorporate this versatile oil into their culinary repertoire. While extra virgin olive oil remains the gold standard for flavor and health benefits in unheated applications, pure olive oil presents a practical and affordable solution for everyday cooking, particularly when high heat is involved.
4. Light Olive Oil: The Neutral Champion for High-Heat Cooking
When exploring the diverse world of olive oils for cooking, "light" olive oil often causes confusion. Contrary to what the name suggests, "light" in this context refers to its mild flavor and pale color, not a reduction in calories or fat content. Light olive oil occupies a unique niche among types of olive oil for cooking due to its high smoke point and neutral taste, making it incredibly versatile for a wide range of culinary applications.
Light olive oil undergoes extensive refining, a process that strips away much of the characteristic olive flavor, aroma, and color. While this might seem detrimental to olive oil purists, it's precisely this neutrality that makes light olive oil a valuable asset in the kitchen. This refined nature results in an oil with the highest smoke point among olive oils – around 470°F (245°C). This makes it ideal for high-heat cooking methods where other olive oils might break down and produce undesirable flavors.
So, how does this refining process work? Olives are pressed to extract the initial oil, much like with extra virgin or virgin olive oils. However, this initial oil then undergoes several refining stages, including degumming, neutralization, bleaching, and deodorization. These processes remove impurities, neutralize acidity, and eliminate strong flavors and colors, resulting in a very light, almost flavorless oil. While this processing removes some of the naturally occurring antioxidants and beneficial compounds found in less refined olive oils, the caloric content remains the same. Light olive oil still provides the same amount of fat and calories per serving as extra virgin olive oil.
The neutral flavor profile of light olive oil is its greatest strength. It serves as a blank canvas, allowing the flavors of your ingredients to shine through without being overpowered by a strong olive taste. This makes it particularly suitable for delicate dishes, baking, and cuisines where a prominent olive oil flavor isn't desired, such as Asian stir-fries or some Mexican dishes. Imagine using a robust extra virgin olive oil in a vanilla cake – the clash of flavors would be jarring. Light olive oil, however, seamlessly integrates without interfering with the delicate sweetness of the dessert.
Here's a breakdown of the pros and cons of using light olive oil:
Pros:
- Neutral Flavor: Its lack of distinct flavor makes it incredibly versatile and suitable for a wide range of cuisines and dishes.
- High Smoke Point: The highest among olive oils, making it ideal for high-heat cooking methods like searing, grilling, and deep-frying.
- Doesn't Interfere with Dish Flavors: Allows the natural flavors of your ingredients to take center stage.
- Excellent for Baking: Provides the necessary fat content in baked goods without imparting an olive oil taste.
- Very Stable for Storage: Has a longer shelf life compared to other olive oils due to its refined nature.
Cons:
- Minimal Nutritional Benefits: The refining process removes some of the beneficial antioxidants and polyphenols found in less refined olive oils.
- Heavily Processed: Undergoes more processing than extra virgin or virgin olive oils.
- No Distinctive Olive Oil Character: Lacks the characteristic flavor and aroma associated with traditional olive oils.
- More Expensive Than Other Neutral Oils: Can be more expensive than other neutral oils like canola or vegetable oil.
When choosing among types of olive oil for cooking, consider light olive oil when a recipe calls for a neutral oil or for high-temperature cooking. It’s a perfect substitute for vegetable oil in most recipes, especially for those sensitive to a strong olive oil taste. Think of dishes like:
- Baking cakes and pastries: Ensures a moist texture without adding unwanted flavors.
- High-heat grilling and searing: Withstands high temperatures without burning or smoking.
- Asian stir-fry dishes: Maintains a clean flavor profile that complements delicate Asian seasonings.
- Professional kitchen applications: Its versatility and high smoke point make it a staple in many professional kitchens.
Light olive oil is a valuable addition to any pantry. While it might not offer the same robust flavor or nutritional benefits as extra virgin olive oil, its neutral taste and high smoke point make it a versatile and reliable choice for various cooking applications. Popular brands offering light olive oil include Bertolli Light, Pompeian Light Taste, Filippo Berio Mild & Light, and Star Light Olive Oil. By understanding its unique properties, you can effectively utilize light olive oil to enhance your culinary creations.
5. Cold-Pressed Extra Virgin Olive Oil: The Gold Standard of Olive Oils
When exploring the diverse world of olive oils for cooking, cold-pressed extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) stands out as the pinnacle of quality. This premium category within extra virgin olive oil represents the purest and most flavorful expression of the olive fruit. If you're seeking the highest nutritional value and the most intense flavor experience, cold-pressed EVOO deserves a prominent place in your kitchen. This type of olive oil is ideal for those seeking the maximum health benefits and flavor complexity that olive oil can offer.
The designation "cold-pressed" refers to a specific extraction method crucial to understanding why this type of olive oil for cooking is so prized. Unlike other methods that employ heat or chemicals, cold-pressing relies solely on mechanical means to extract the oil from the olives. This process involves crushing the olives into a paste and then pressing them to separate the oil from the pulp. Critically, the entire process is carried out at temperatures below 80.6°F (27°C). This low-temperature extraction is paramount to preserving the delicate aroma, vibrant flavor, and rich nutritional compounds inherent in the fresh olives. Heat can degrade these desirable qualities, resulting in a less flavorful and less nutritious oil.
The meticulous process yields an oil with a remarkably complex flavor profile, often described as peppery, grassy, or fruity, depending on the olive varietal and terroir. This intense flavor and aroma are a direct result of the preserved volatile aromatic compounds and antioxidants, which are more abundant in cold-pressed EVOO. Among these beneficial compounds are polyphenols, powerful antioxidants linked to various health benefits, including reduced inflammation and a lower risk of chronic diseases. In fact, cold-pressed EVOO consistently boasts the highest polyphenol content among all types of olive oil for cooking.
The benefits of choosing cold-pressed EVOO are numerous. From a health perspective, its high antioxidant and polyphenol content makes it a valuable addition to a balanced diet. Its richness in monounsaturated fats contributes to heart health, while the anti-inflammatory properties may offer protection against various ailments. From a culinary perspective, the intense and complex flavors of cold-pressed EVOO elevate dishes to a gourmet level. It can transform a simple salad into a culinary masterpiece or add a finishing touch to grilled meats and vegetables.
However, this premium quality comes at a price. Cold-pressed EVOO is generally the most expensive type of olive oil for cooking. Its meticulous production process and limited yield contribute to the higher cost. Furthermore, the strong flavor profile may not appeal to all palates, especially those accustomed to milder oils. It's also important to note that its low smoke point makes it unsuitable for high-heat cooking methods like frying. Exposure to high temperatures can degrade the oil and diminish its flavor and nutritional value.
To fully appreciate the nuances of cold-pressed EVOO, consider using it in applications where its flavor can shine. Gourmet restaurant finishing oil, artisanal bread dipping, premium salad dressings, and high-end culinary competitions are all excellent examples of where this type of olive oil for cooking excels. Think of it as a condiment rather than a cooking oil. Drizzling it over a finished dish enhances the flavors without subjecting the oil to damaging heat.
When purchasing cold-pressed EVOO, look for indicators of quality. Checking the harvest date is crucial, as freshness plays a vital role in flavor and nutritional value. Certifications like "Protected Designation of Origin" (PDO) or "Protected Geographical Indication" (PGI) can further assure authenticity and quality. Reputable brands like Olea Estates, Partanna, McEvoy Ranch, and Boundary Bend Estate are known for their commitment to producing high-quality cold-pressed EVOO.
To maximize the shelf life and preserve the delicate flavors, store cold-pressed EVOO in a cool, dark place, away from heat and light. Avoid storing it near the stove or in direct sunlight.
In conclusion, while cold-pressed EVOO may be a more expensive option among the types of olive oil for cooking, its exceptional flavor, aroma, and nutritional benefits make it a worthwhile investment for discerning consumers. Its unparalleled quality and versatility justify its place as the gold standard of olive oils. By understanding its unique characteristics and following the tips above, you can fully appreciate the culinary and health benefits of this exceptional oil.
6. Single-Origin/Estate Olive Oil: A Taste of Terroir
When exploring the diverse world of olive oils for cooking, single-origin/estate olive oils represent the pinnacle of quality, traceability, and unique flavor profiles. Much like the world of fine wines, these oils are crafted from olives grown within a specific geographic region or even a single estate, allowing the distinct characteristics of the terroir to shine through. If you're looking to elevate your culinary creations with olive oil that boasts both exceptional quality and a captivating story, single-origin/estate oils deserve a place in your pantry. This type of olive oil offers a unique experience for discerning palates and those seeking a deeper connection to the origins of their food. Understanding its nuances can truly enhance your appreciation for this versatile ingredient and its potential to transform your cooking.
The concept of single-origin/estate olive oil revolves around showcasing the unique terroir of a specific location. Terroir, encompassing the soil composition, climate, altitude, and even the surrounding vegetation, imparts distinct characteristics to the olives grown in that area. This, in turn, translates into an olive oil with a flavor profile that reflects its origin. Often, these oils are made from a single olive variety, further emphasizing the unique qualities of that specific cultivar and its interaction with the local environment. For example, a Tuscan estate oil made solely from Frantoio olives will possess different characteristics than a Kalamata region oil made from Koroneiki olives, even though both are single-origin oils. This emphasis on origin and variety makes single-origin oils a fascinating exploration of the diverse world of olive oil flavors.
The production process for single-origin/estate oils is often characterized by small-batch production and meticulous attention to detail. Harvest date transparency is also a common feature, allowing consumers to understand the freshness and seasonal variations of the oil. This artisanal approach, coupled with strict quality control measures, often results in oils of superior quality. Producers like Castello di Ama in Tuscany, renowned for their elegant and complex olive oils, exemplify the dedication to quality and terroir expression found in the world of single-origin production. Similarly, Cobram Estate in Australia has demonstrated how a specific terroir can influence olive oil production even in regions not traditionally associated with olive growing. McEvoy Ranch in California and Núñez de Prado in Spain also stand as testaments to the global reach of high-quality, single-origin olive oil production.
Pros of Choosing Single-Origin/Estate Olive Oil:
- Unique and Distinctive Flavors: Experience the nuances of a specific terroir reflected in the oil's flavor profile, from peppery and robust to fruity and delicate.
- Quality Traceability and Transparency: Know exactly where your oil comes from and how it was produced, fostering trust and confidence in the product.
- Supports Local/Regional Producers: Contribute to the economic sustainability of small-scale producers and preserve traditional olive growing practices.
- Often Superior Quality Control: Smaller production scales often allow for greater attention to detail and quality control throughout the process.
- Educational Tasting Experience: Engage with the nuances of different olive varieties and terroirs, expanding your culinary horizons.
Cons of Choosing Single-Origin/Estate Olive Oil:
- Higher Price Point: Reflecting the artisanal production methods and limited quantities, these oils are typically more expensive than blended oils.
- Limited Availability: Single-origin oils may not be as readily available as mass-produced blended oils.
- Seasonal Availability Variations: Production is subject to seasonal variations, and certain oils may only be available during specific times of the year.
- May Require Acquired Taste: The distinct and sometimes intense flavors of single-origin oils may require an adjustment for palates accustomed to milder oils.
- Less Versatile than Blended Oils: The unique flavor profiles of some single-origin oils may not be suitable for all types of cooking.
Tips for Exploring Single-Origin/Estate Olive Oils:
- Research the Producer's Reputation: Look for producers committed to sustainable practices and quality production.
- Try Small Bottles First to Test Preference: Experiment with different origins and varieties to discover your favorite flavor profiles.
- Use for Special Occasions and Dishes: Elevate your culinary creations by using these premium oils for finishing dishes or in recipes where the olive oil flavor takes center stage.
- Pair with Foods from the Same Region: Enhance the flavors of your dishes by pairing the olive oil with ingredients from its region of origin. For example, a Tuscan olive oil pairs beautifully with a classic Tuscan tomato bruschetta.
By understanding the characteristics and nuances of single-origin/estate olive oils, you can make informed choices that enhance your cooking and provide a unique culinary experience. Whether you are a seasoned olive oil enthusiast or just beginning to explore the different types of olive oil for cooking, discovering the world of single-origin oils is a rewarding journey for any food lover.
7. Flavored/Infused Olive Oil
Flavored or infused olive oils offer a convenient and exciting way to elevate your cooking with the combined benefits of healthy fats and captivating aromas. These specialty oils start with a base of extra virgin or virgin olive oil, which is then infused with natural flavors like herbs, spices, citrus fruits, or even chili peppers. This infusion process can occur during or after the pressing of the olives, resulting in a versatile ingredient that can transform ordinary dishes into culinary masterpieces. Whether you're drizzling it over a finished dish or using it as a cooking medium, flavored olive oil adds a depth of flavor that eliminates the need for numerous separate seasonings. This makes it a particularly appealing option among the various types of olive oil for cooking.

The beauty of flavored olive oils lies in the sheer variety of flavor combinations available. From the bright, zesty notes of lemon-infused oil to the robust warmth of garlic or rosemary, there's a flavor profile to complement virtually any cuisine. Popular varieties include lemon, garlic, rosemary, and chili-infused oils, but artisanal producers are constantly pushing the boundaries with innovative combinations like blood orange, truffle, and even smoked paprika. This makes infused oils a valuable addition to any kitchen seeking to explore different types of olive oil for cooking.
Several features distinguish flavored olive oils. Primarily, they are made from a high-quality virgin or extra virgin olive oil base, ensuring you receive the health benefits associated with these oils. The infusion process, ideally using natural ingredients, adds a concentrated layer of flavor. Both artisanal and commercial options are readily available, allowing you to explore small-batch creations or readily accessible supermarket brands. These oils truly shine in their specialized culinary applications, providing a shortcut to complex flavor profiles without requiring extensive preparation.
There are many pros to using flavored olive oils. They offer a convenient flavor enhancement, saving you time and effort in the kitchen. Their versatile culinary applications range from marinades and dressings to finishing drizzles and cooking mediums. They eliminate the need for multiple separate seasonings, streamlining your cooking process. They also unlock creative cooking possibilities, encouraging experimentation and exploration of different flavor combinations. Finally, their unique and specialized nature makes them thoughtful and gift-worthy specialty items.
However, flavored olive oils also have a few drawbacks. They generally come at a higher cost than plain olive oil due to the added ingredients and specialized production. The added ingredients also contribute to a limited shelf life, typically between 6-12 months. The intensified flavors may not suit all palates or dishes, so experimentation is crucial. The quality can vary significantly between brands, with some manufacturers opting for artificial flavorings instead of natural infusions. It's crucial to carefully review the ingredient list to ensure the product meets your standards.
Consider using lemon-infused oil to brighten up seafood dishes, garlic oil to add pungent depth to pasta and pizza, rosemary oil to enhance roasted vegetables, and chili oil to bring the heat to spicy applications. These are just a few examples of how flavored olive oils can transform your cooking.
To get the most out of your flavored olive oil experience, prioritize oils infused with natural ingredients over those with artificial flavorings. Use the oil within 6-12 months for optimal flavor and quality. Start with small amounts when experimenting with a new oil to gauge its intensity and adjust accordingly. For a truly personalized touch, consider making your own infused olive oil by gently heating high-quality extra virgin olive oil with your desired herbs or spices. This allows for complete control over the flavor profile and ensures the use of fresh, natural ingredients. Companies like O Olive Oil stores, Williams Sonoma, local artisanal producers, and specialty markets like Eataly have popularized and made these flavorful oils widely accessible. By understanding the nuances of flavored olive oils, you can make informed choices about incorporating these dynamic ingredients into your culinary repertoire and explore the diverse world of types of olive oil for cooking.
Comparison of 7 Olive Oil Types for Cooking
| Type | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) | Moderate – mechanical cold-pressing without chemicals | Requires fresh olives, fast processing within 24 hrs | Highest flavor and nutritional quality; rich antioxidants | Finishing dishes, salad dressings, low-heat sautéing | Superior flavor; high antioxidants; healthy fats |
| Virgin Olive Oil | Moderate – mechanical extraction, slightly higher acidity | Less stringent timing and quality control | Good flavor and nutritional benefits, moderate antioxidants | Everyday cooking, medium-heat sautéing, baking | Balanced quality and cost; suitable for cooking |
| Pure Olive Oil (Refined) | Lower – involves refining and blending virgin oils | Refining facilities and blending process | Neutral flavor, higher smoke point, longer shelf life | High-heat cooking, frying, baking, stir-frying | Versatile for all cooking; high smoke point |
| Light Olive Oil | Low – highly refined with intensive processing | Requires advanced refining technology | Neutral flavor, highest smoke point, minimal nutrients | Baking, grilling, frying, neutral-flavor recipes | Highest smoke point; neutral taste; stable storage |
| Cold-Pressed Extra Virgin Olive Oil | High – strict temperature control (<27°C) during pressing | Premium equipment and careful handling | Maximum nutrient preservation, intense flavor | Gourmet finishing, premium dressings, health focus | Pinnacle of quality and antioxidants; intense flavor |
| Single-Origin/Estate Olive Oil | Variable – small-batch, terroir-specific production | Specialized farms and traceability systems | Unique terroir-driven flavors, artisanal quality | Gourmet applications, tastings, regional pairings | Distinctive flavors; quality transparency |
| Flavored/Infused Olive Oil | Moderate – infusion after or during pressing | Additional natural flavor ingredients | Enhanced flavor profiles, versatile culinary uses | Finishing dishes, marinades, dressings, gifts | Convenient flavor enhancement; creative options |
Elevating Your Cooking with the Right Olive Oil
From the vibrant, peppery notes of a single-origin extra virgin olive oil to the subtle flavors of light olive oil, understanding the different types of olive oil for cooking can truly elevate your culinary creations. We've explored several key varieties, including extra virgin olive oil (EVOO), virgin olive oil, pure olive oil, and even flavored options, each with its ideal uses and benefits. Remember that factors like smoke point, flavor profile, and extraction method play crucial roles in determining which type of olive oil best suits your cooking needs. Mastering these nuances allows you to not only enhance the taste of your dishes but also reap the potential health benefits associated with high-quality olive oils. By choosing the right type of olive oil for cooking, you're not just adding an ingredient; you're adding a layer of flavor, complexity, and healthfulness to your meals.
Want to further refine your understanding of olive oil and explore its vast culinary potential? Visit Learn Olive Oil for in-depth information on various types of olive oil for cooking, along with tips, recipes, and resources to help you become a true olive oil connoisseur. Start your flavorful journey today!

Leave a comment